Figure 5.
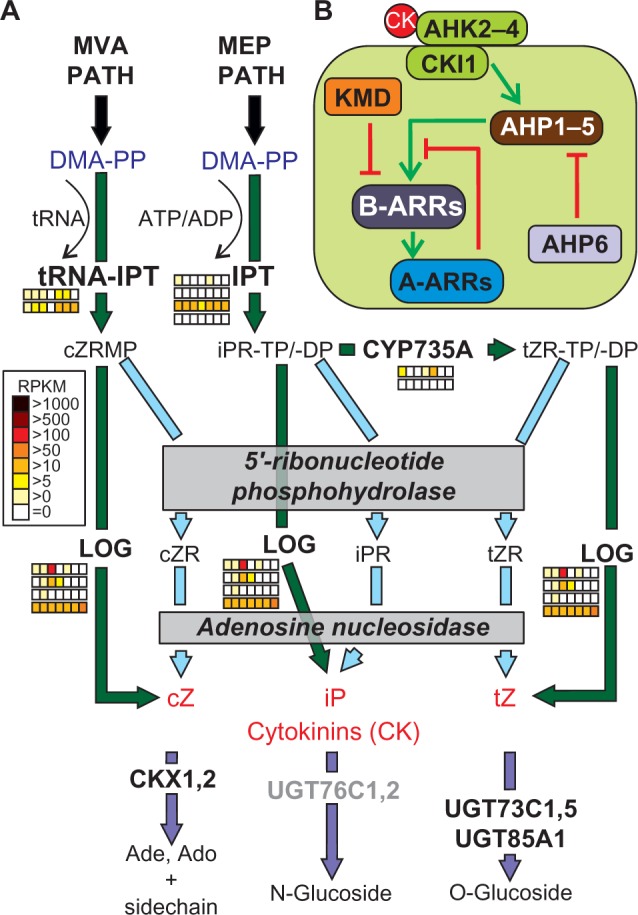
Pathways of cytokinin synthesis and signaling. (A) The precursor of cytokinin synthesis is DMA-PP, which is derived from the MVA or MEP pathways. The intermediate products cZRMP, iPRTP/-DP, or tZRTP/-DP are converted to the final products such as cZ, iP, or tZ (red) by the action of LOG or by yet not clearly defined 5′-ribonucleotide phosphohydrolases and adenosine nucleosidases. For further details, see text. The arrows are colored according to the species in which the enzymes were found (Fig. 1A). Expression of the identified co-orthologues in tomato is shown as explained in Figure 2. Genes coding for enzyme activities not expressed by any orthologue are colored in gray. (B) The components involved in cytokinin signaling are presented as interaction scheme.
Abbreviations: Proteins: IPT, isopentenyltransferase; CYP735A, cytochrome P450, family 735, subfamily A; LOG, LONELY GUY; UGT73C, UDP-glucosyl transferase 73C; UGT85A, UDP-glucosyl transferase 85A; CKX, cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase; AHK, Arabidopsis histidine kinase; CKI, cytokinin-independent; AHP, histidine-containing phosphotransmitter; ARR2, response regulator; KMD, KISS ME DEADLY. Metabolites: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; DMA-PP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; cZRMP, cZR 5′ monophosphate; iPRTP, iPR 5′ triphosphate; tZRTP, tZR 5′ triphosphate; cZR, cis-zeatin riboside; iPR, isopentenylribose; tZR, trans-zeatin riboside; cZ, cis-zeatin; iP, isopentenyladenine; tZ, trans-zeatin.
