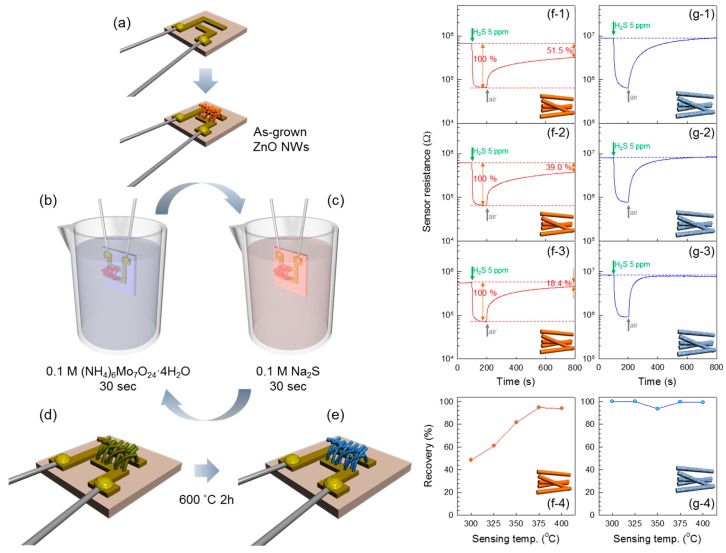
Figure 5.
(a–e) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process of Mo-doped ZnO NW network gas sensors. Sensing transients of pure and Mo-doped ZnO NW network gas sensors to 5 ppm H2S at 300, 325, and 350 °C: (f-1) ZnO NW sensor, 300 °C; (f-2) ZnO NW sensor, 325 °C; (f-3) ZnO NW sensor, 350 °C; (g-1) Mo-doped ZnO NW sensor, 300 °C; (g-2) Mo-doped ZnO NW sensor, 325 °C; and (g-3) Mo-doped ZnO NW sensor, 350 °C; (f-4,g-4) Recovery (%) = (Rair-recovery − Rgas-H2S)/(Rair-fresh − Rgas-H2S) × 100 (%) of pure and Mo-doped ZnO NW sensors at 300–400 °C (where, Rair-fresh: sensor resistance in air before exposure to H2S, Rgas-H2S: sensor resistance in 5 ppm H2S, and Rair-recovery: sensor resistance in air after 10 min exposure to air). Reproduced from [88] with permission. Copyright (2014) The Royal Society of Chemistry.