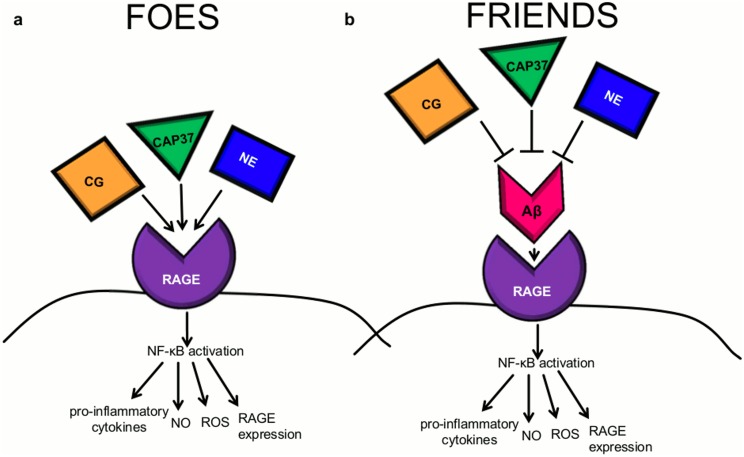
Fig 11. Proposed model for the modulation of RAGE signaling by CAP37, neutrophil elastase, and cathepsin G.
(a) CAP37, neutrophil elastase (NE), and/or cathepsin G (CG) may act as RAGE agonists to induce a cell signaling cascade that leads to activation of the transcription factor NF-κB. Activation of NF-κB could then stimulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and pro-oxidants including reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) as well as RAGE itself. In this way, the neutrophil proteins would likely act as foes in the course of chronic inflammatory disease such as AD. (b) CAP37, neutrophil elastase, and cathepsin G may prevent the Aβ1-42-RAGE interaction and the corresponding NF-κB signaling cascade. In this way, the neutrophil proteins would act as friends to prevent chronic neuroinflammation driven by Aβ1–42 activation of RAGE.