Fig. 2.
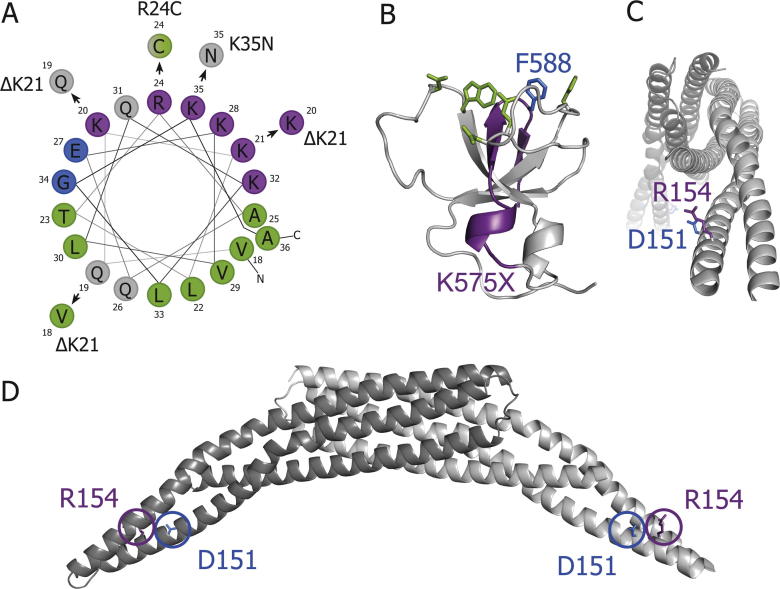
Structural consequences of CNM-linked mutations in BIN1. A. Helical wheel projection of residues 18-36 (amphipathic helix) from human BIN1 and likely new positioning due to ΔK21, R24C and K35N. B. Affected residues of truncation of SH3 domain. Lacking parts in human K575X mutant in violet; human F588 (blue) is part of dynamin binding face (green); crystal structure from rat BIN1 (Owen et al., 1998). Charged residues are marked in violet (positive) and blue (negative), hydrophobic residues in green and polar uncharged residues in grey. C, D. D151 and R154 are on the tip of the BIN1 BAR domain dimer and point sideways. Visualisation of a BAR domain dimer from the front, with each monomer in a different grey shade (C). Side view (D).