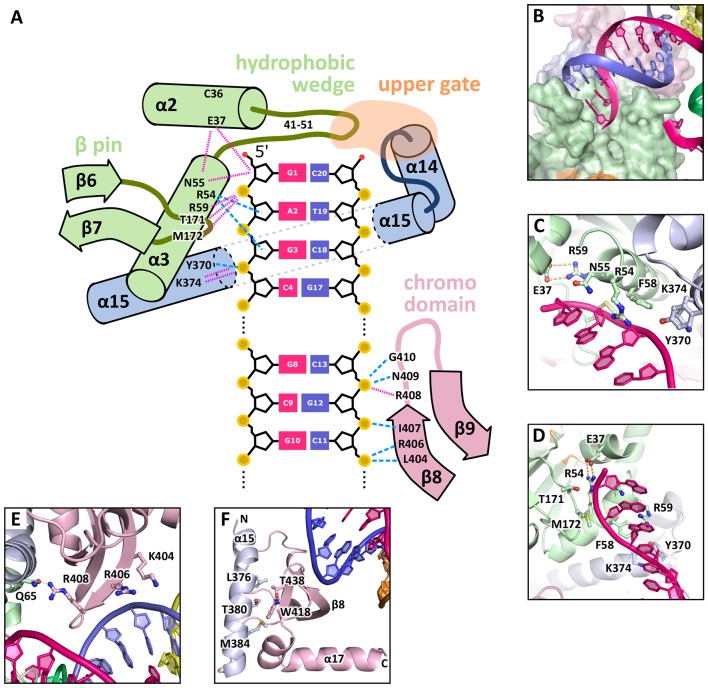
Figure 4. DNA interactions in the GEN1-DNA complex.
(A) Schematic of the GEN1-DNA interactions at the upstream interface. The coloring is the same as in Figure 1. The nuclease core (green and blue) interacts with the uncleaved strand and the chromodomain (pink) contacts the complementary strand. Hydrogen bonds are shown with blue dashed lines and van-der-Waals contacts are in red dotted lines. (B) Interactions at the hydrophobic wedge. The end of the DNA double helix docks onto the hydrophobic wedge formed by helices α2 and α3. (C/D) Interactions with the uncleaved strand in two views. All key residues form sequence-independent contacts to the DNA backbone. R54 reaches into the minor groove of the DNA. The complementary DNA strand has been removed for clarity (E/F) Interactions of the chromodomain with the complementary strand in two views. The backbone of residues 406–410 (β-hairpin β8-β9) abuts the DNA backbone. R406 has a supporting role in the interaction and R408 forms a polar interaction with Q65, which establishes a connection between the chromodomain and the nuclease core. Helix α15 makes hydrophobic interactions with the aromatic cage and thus blocks it.