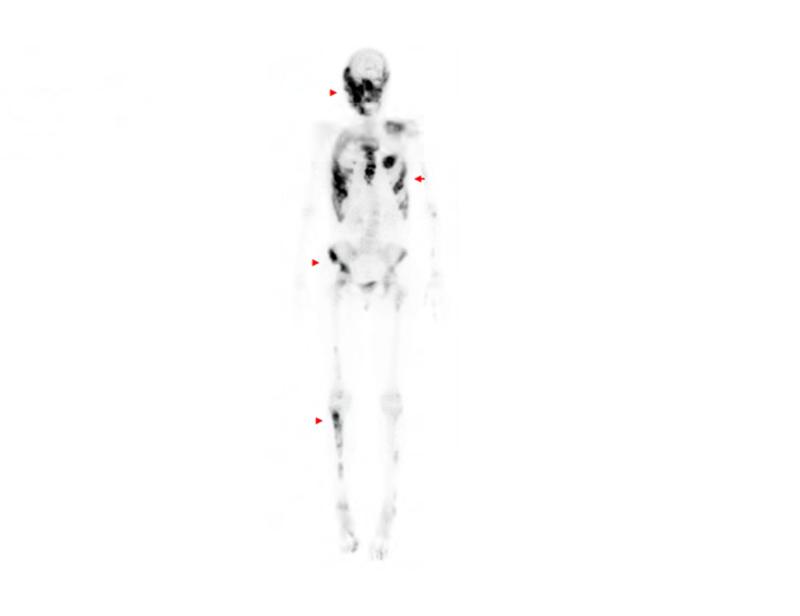
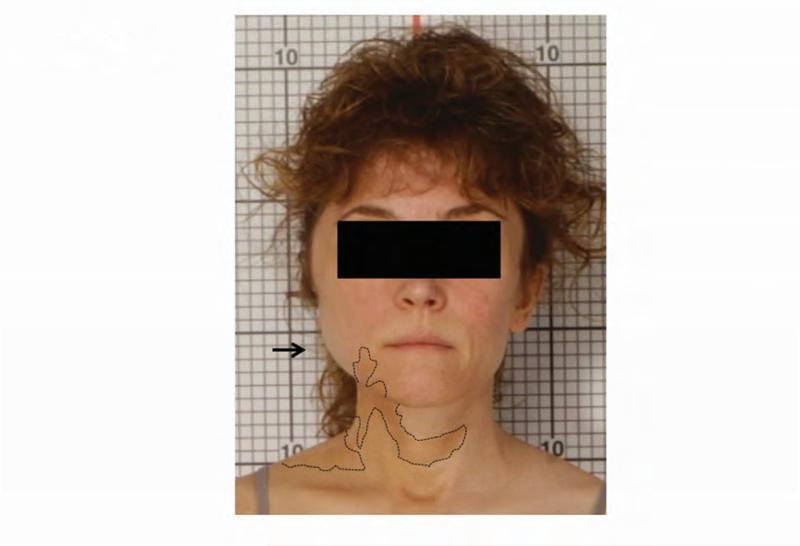
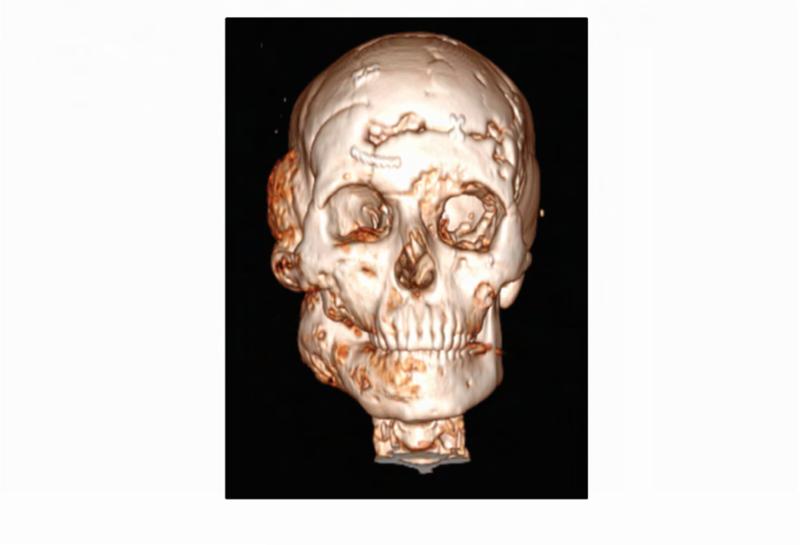
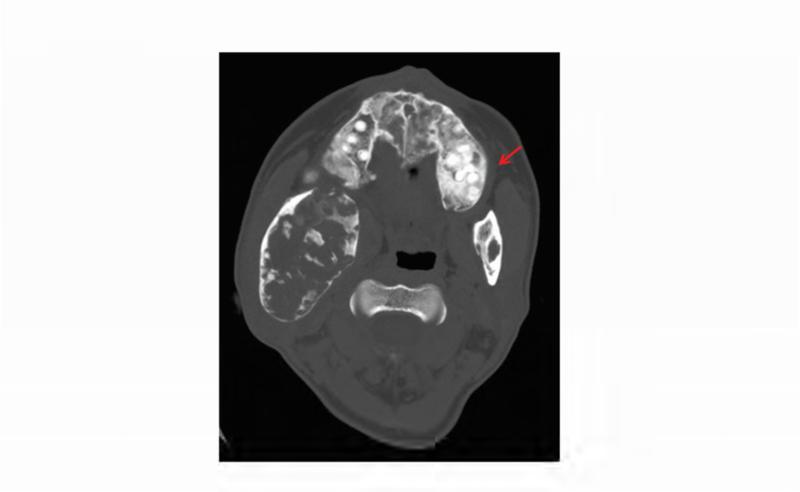
Figure 1. Case 1 clinical images.
A. 99Technetium bone scintigraphy shows multiple areas of increased uptake consistent with fibrous dysplasia involving the skull, ribs, pelvis, and lower extremities (red arrowheads). B. Photograph demonstrating asymmetric expansion of the right mandible (black arrow). Note the café-au-lait macule involving the jaw, shoulder and neck with characteristic features, including jagged, “coast of Maine” borders and location respecting the midline of the body (dashed lines). C. Three-dimensional computed tomography demonstrates facial asymmetry with multiple expansile lesions particularly affecting the right side of the skull. D. Axial computed tomography images show extensive craniofacial fibrous dysplasia demonstrating the characteristic “ground glass” appearance with multiple areas of radiolucency. Note the left maxilla and alveolar ridge with extensive fibrous dysplasia involvement encasing the left maxillary first and second molars (ADA #14 and 15)(red arrow).