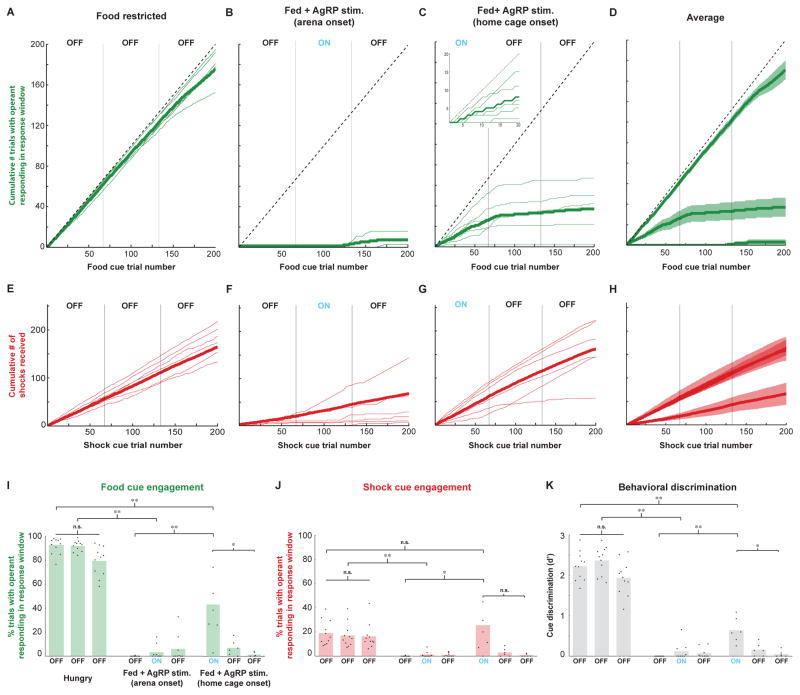
Figure 3. Quantification of engagement in the visual discrimination task across hunger states and AgRP neuron photostimulation protocols.
(A–D): Cumulative number of pokes during the response window, following termination of the food cue, obtained throughout 600 trial sessions in the food-restricted (A), arena photostimulation onset (B), and home cage photostimulation onset (C) conditions, together with the means ± SE across mice for each condition (D). (E–H): Similar to A–D, but for cumulative shocks received. Note that, for each shock cue presentation, it was possible to receive up to two shocks, one for poking following shock cue offset, and one for being off of the safety platform at shock cue offset. (I) Food cue engagement, defined as the percentage of food cue trials in which mice received a food reward, is high in food-restricted (FR) mice (left), and low both in both fed mice and in fed mice receiving AgRP neuron photostimulation that began after arena placement (middle). In contrast, fed mice that received AgRP neuron photostimulation beginning in the home cage, prior to arena entry, showed an intermediate level of food cue engagement (right). Dots: mean engagement for each mouse; bars: grand average across mice. (J) Mice also displayed differential engagement following the shock cue across experimental protocols. (K) The discriminability index, d′, which measures a mouse’s ability to perform selective operant responding following the food cue but not following the other cues, was also significantly elevated in food-restricted mice, and in fed mice that received AgRP photostimulation prior to arena entry, as compared to fed mice in all other conditions. **p<0.01/n, *p<0.05/n, n.s., not significant; Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (n = 9); Wilcoxon rank-sum test for independent samples. See also Figures S3 and S4.