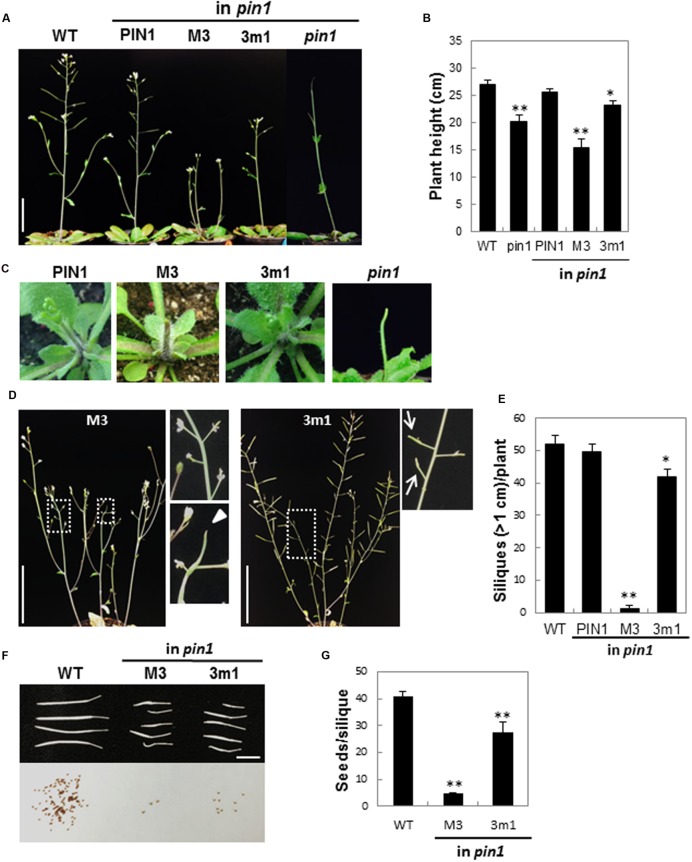
FIGURE 4.
Effect of M3 or 3m1 mutation of PIN1 on reproductive development. (A) Inflorescence stems of WT, homozygous pin1, and homozygous pin1 complemented with PIN1 (ProPIN1:PIN1:GFP), M3PIN1(M3, ProPIN1:M3PIN1:GFP), and 3m1PIN1 (3m1, ProPIN1:3m1PIN1:GFP). Bar = 5 cm. (B) Average height of the plants in (A). Data represent means ± SE (n = 7–10). Differences are significant from WT value at ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.005. (C) Early developing inflorescence stems. (D) Defects in reproductive organs by M3 or 3m1 mutation. Arrowhead indicates the defect in the stem tip. Arrows indicate defects in siliques. (E) Number of silique over 1-cm long. Data represent means ± SE (n = 5–8 plants). Differences are significant from WT value at ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.005 in t-test. (F) Siliques and seeds from WT and strong phenotypic siliques of M3 and 3m1 plants. Seeds were harvested from the siliques shown in the upper photograph. Bar = 5 mm. (G) Number of seeds per silique. Data represent means ± SE (n = 8–20 siliques). Differences are significant from WT value at ∗∗P < 0.005 in t-test.