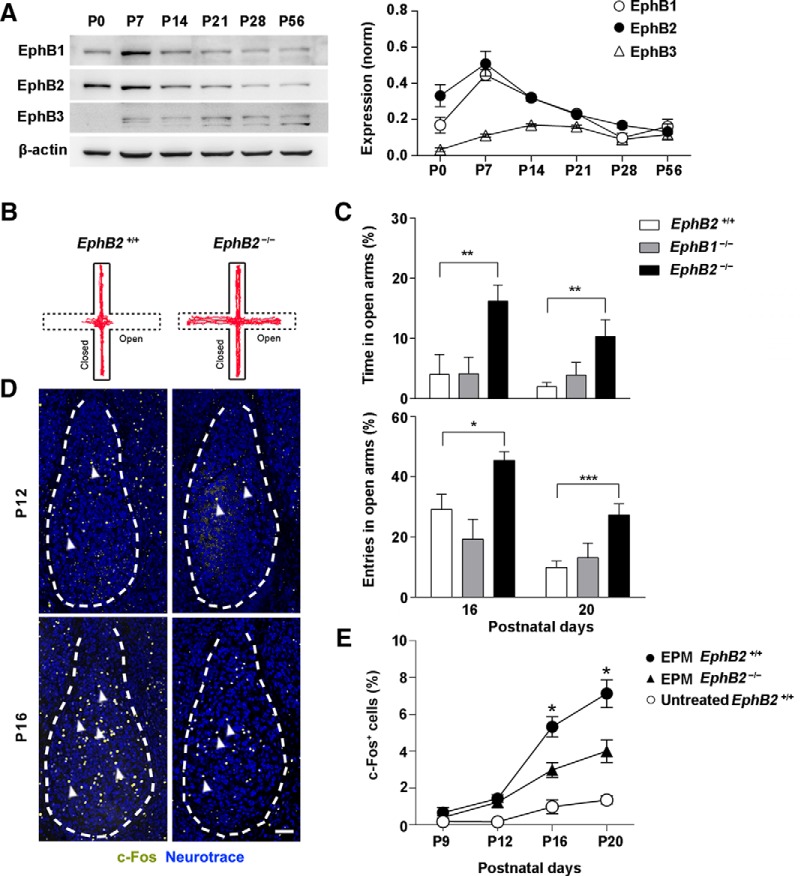
Figure 1.
EphB2 is required for innate fear response of juvenile mice in EPM trials. A, The expression levels of EphB1, EphB2, and EphB3 proteins were analyzed by Western blotting of amygdala lysates from P0–P56 wild-type mice. B, Representative animal track of EPM for EphB2+/+ and EphB2−/− mice at P16. C, EphB2−/− but not EphB1−/− mice spent significantly more time and higher entry probability in the open arms than wild types at P16 and P20 (n = 20–25 per group). D, c-Fos activation was decreased in BLA neurons of EphB2−/− mutants (arrowheads) at P16 following EPM behavior trial. Scale bar, 100 μm. E, Quantification of c-Fos-positive cells (percentage of total neurotrace positive cells) in BLA from P9 to P20 following EPM behavioral trial for EphB2+/+ and EphB2−/− mice or an untreated control procedure in which the wild-type mice were exposed solely to the context and normal handling but without EPM treatment. n = 6–7 mice for each group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.