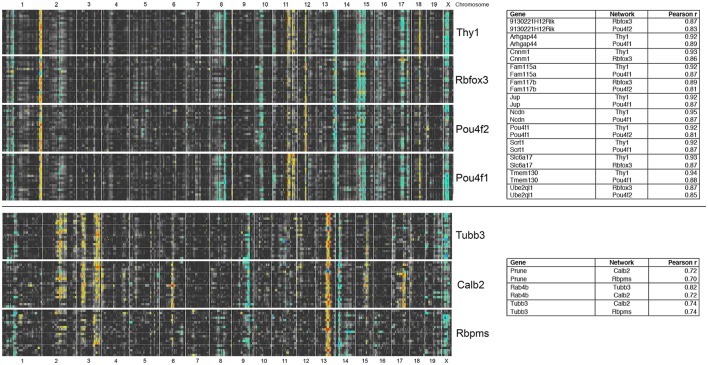
Figure 3.
RGC markers segregate into two major correlation networks. For each of the general RGC markers on the right, the eQTL curve for the 20 highest correlated genes was plotted as a heat map. In these, the LRS/LOD score is given in pseudocolors: A yellow to red gradient identifies a transcript whose expression is higher in strains with a B haplotype at that locus (allele origin from C57BL/6J), whereas a green to blue gradient represents a transcript whose expression is higher in strains with the D haplotype (allele origin from DBA/2J). There are several strong and sharp trans-bands extending across Thy1, Rbfox3, Pou4f2, and Pou4f1, such as on distal Chromosome 1 or 13. There are also trans-bands extending across Tubb3, Calb2, and Rbpms on mid Chr. 13 and proximal Chr. 14. No overlap is present between the genes separated by the black line, indicating that RGC markers segregate into two major independently regulated gene networks. The panel on the right lists genes that are found in more than one of the top 20 correlations. For example, Arhgap44 is present in the 20 highest correlates for both Thy1 and Pou4f1.