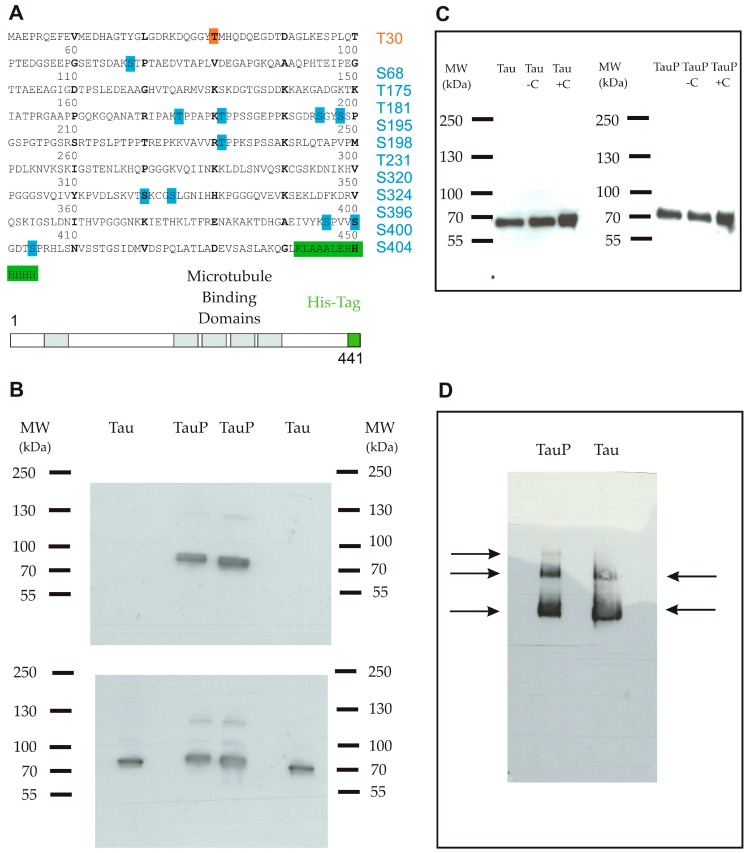
Figure 1.
(A) Primary sequence of the full-length recombinant monomeric Tau protein 1-441 isoform (2N4R) coupled with a C-terminal His-tag (6× His). The protein comprised one phosphorylation site for the low phosphorylated form (orange) and 11 phosphorylation sites for the highly phosphorylated form (blue); (B) Western blot using an anti-phosphoT231 antibody. Upper panel shows a band only for the highly phosphorylated form. Lower panel is a control with an anti-Tau antibody and shows that both proteins were correctly loaded in duplicate; (C) Western blot using an anti-His-tag antibody shows that the Tau protein remained in a monomeric form in the purified stock (well 1), after an incubation of 6 h in medium only (well 2) and after an incubation of 6 h in the presence of cortical cells (C) (well 3) for low (left) and highly phosphorylated (right) Tau proteins; (D) Blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) followed by immunodetection using an anti-Tau antibody shows three bands for the highly phosphorylated form (from the top-down: trimers, dimers and monomers) and two bands for the low phosphorylated form (from the top-down: dimers and monomers).