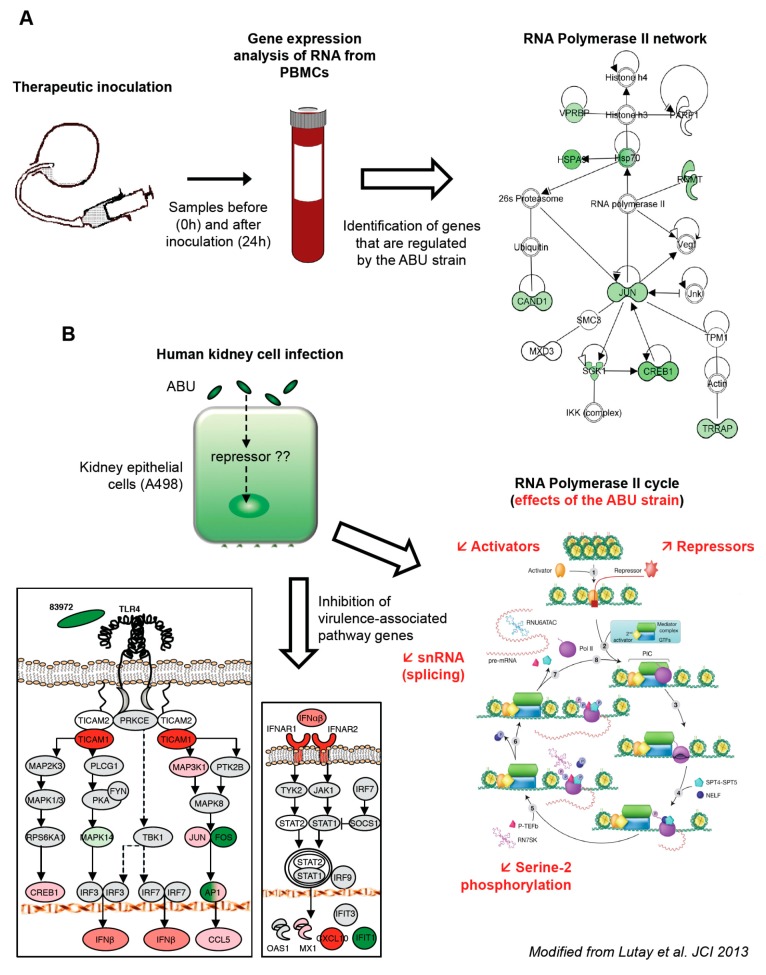
Figure 1.
Suppression of gene expression in inoculated patients and infected human kidney cells. (A) Schematic of therapeutic inoculation with the ABU strain E. coli 83972, which established ABU in the inoculated patients. RNA was extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) before and 24 h after intravesical inoculation. Significantly regulated genes were identified by transcriptomic analysis. Genes in the Pol II network were suppressed, by the ABU strain; (B) Human kidney epithelial cells (A498) were infected with the ABU strain E. coli 83972 and significantly regulated genes were identified by transcriptomic analysis, compared to uninfected cells. Pol II transcription cycle with gene categories regulated by ABU indicated in red. ABU infection affected different steps in the Pol II cycle, including chromatin opening, escape from pausing and pre-mRNA splicing. The ABU strain failed to activate/inhibit the pathology-associated TLR4 and IFN-β pathways. Adapted from Lutay et al. [14].