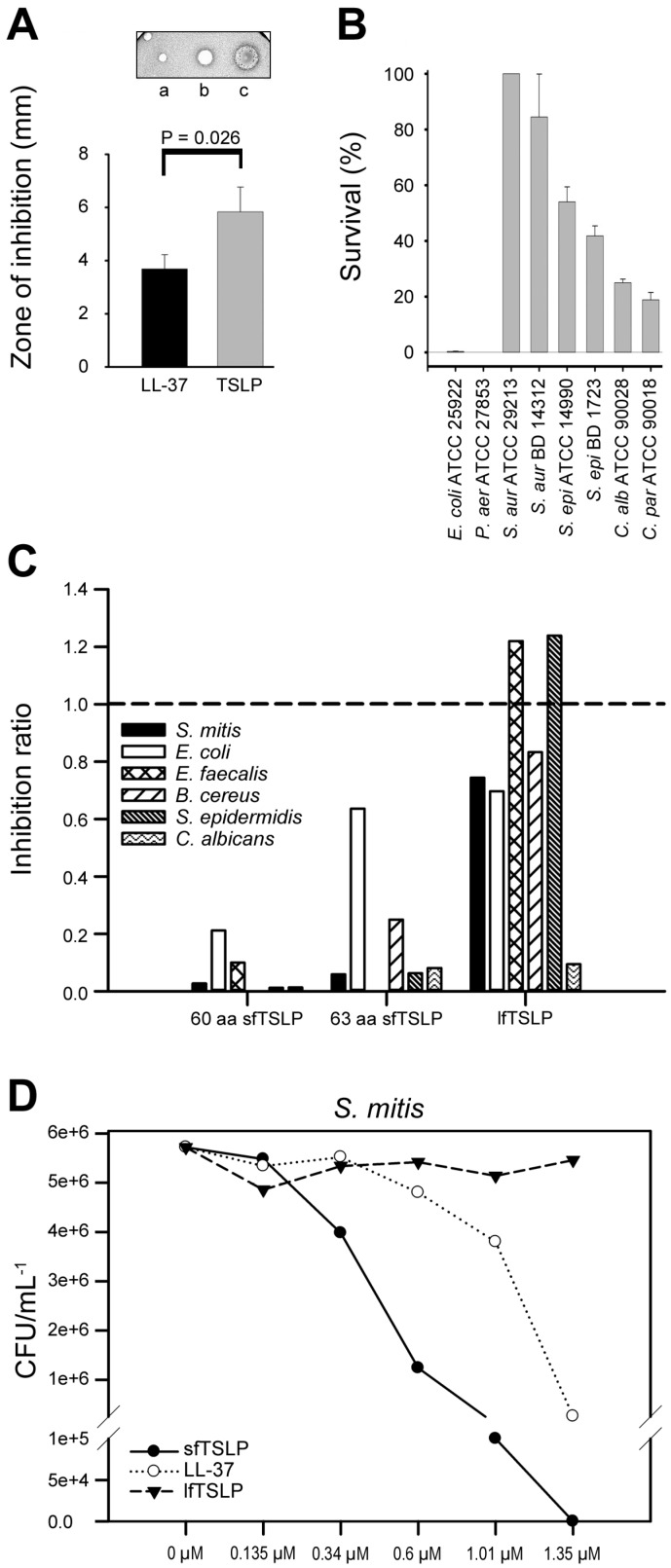
Figure 5.
Antimicrobial activity of short and long forms of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (sfTSLP and lfTSLP). (A) lfTSLP exhibited a larger zone of inhibition of growth of Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 in comparison with LL-37: (a) control; (b) 10 µM LL-37; and (c) 10µM TSLP. Mean values and standard deviations (n = 4). (B) In a viable count assay, indicated bacterial (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis) and fungal isolates (Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis) were subjected to 2 µM of TSLP. The number of cfu was registered. (C) Suspensions of the indicated bacterial and fungal species were treated for 2 h with 60 amino acid (aa) sfTSLP, and 63 aa sfTSLP or lfTSLP peptide at a concentration of 1.35 mM before being plated on agar. Colony-forming units per ml were determined after incubation overnight. The values were normalized to the levels obtained without the addition of test peptides (broken line). (D) Suspensions of Streptococcus mitis were treated with equimolar concentrations of 60 aa sfTSLP, LL-37, or lfTSLP and analyzed as in C. From: [7] (A,B) and [5] (C,D).