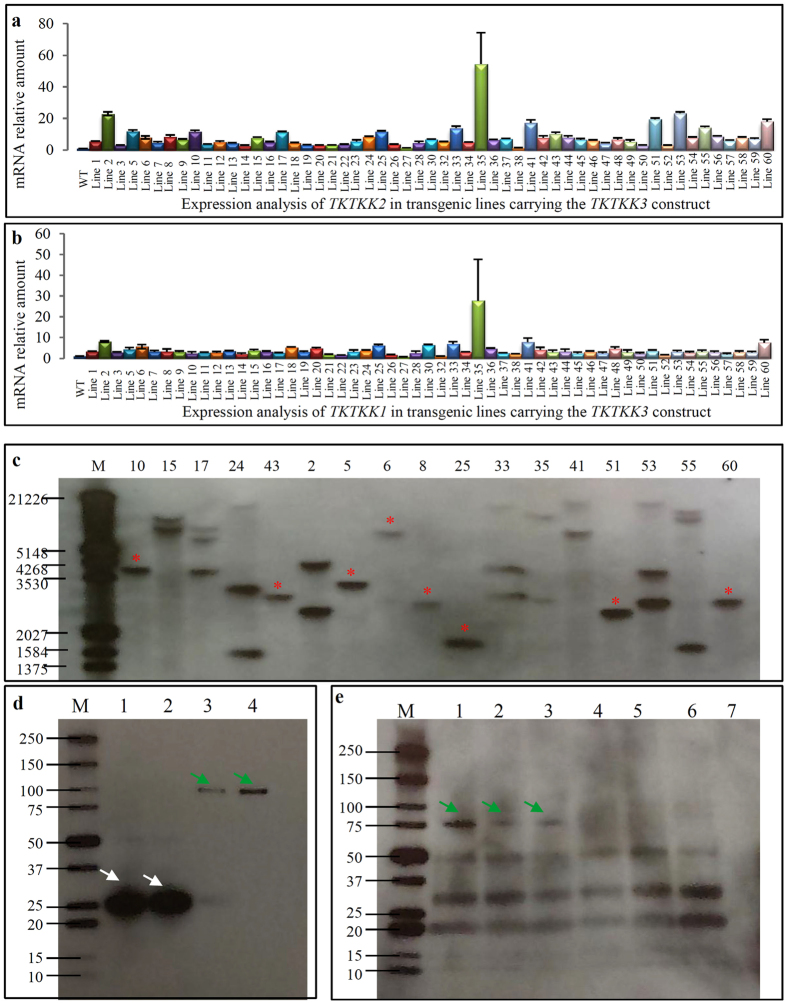
Figure 4. Molecular characterization of 35S::TKTKK3 transgenic plants and western blot hybridization.
(a,b) show the bar diagrams of expression patterns of both genes TKTKK1 and TKTKK2 in 55 35S::TKTKK3 transgenic plants by qRT-PCR, respectively. (c) Southern blot hybridization for detecting copy numbers of T-DNA insertion. DNA samples (line numbers were labelled on the top of the panel) were digested by the restriction enzyme EcoRV and were then transferred into nylon member for hybridization with the HPT probe. The red stars “*” indicated the lines with single copy number of T-DNA insertion. (d,e) Western blot hybridization using crude proteins from E. coli (d) and T2 rice grains (e), respectively. The “M” in (d,e) indicates the protein marker used for the hybridization. The numbers in (d) indicate the crude proteins extracted from E. coli carrying the plasmid pGEX-6P-1 (1 and 2) and pGEX-6P-1::TKTKK1 (3 and 4). The white arrows indicated the GST expression in the E. coli carrying the plasmid pGEX-6P-1. The green arrows indicated the GST fusion protein expression in the E. coli carrying pGEX-6P-1::TKTKK1. The numbers in (e) indicate the different transgenic lines used for crude proteins extraction from rice seeds. Three lines (1, line 9, 2, line 14 and 3, line 21) were from 35S::TKTKK1. Line 46 (indicated by 4) and Line 5 (indicated by 5) were from 35S::TKTKK2 and 35S::TKTKK3, respectively. The number 6 indicates WT and 7 indicates negative control. The green arrows indicated the stable expression of TKTKK1 protein in lines 9, 14 and 21 by Western blot hybridization.