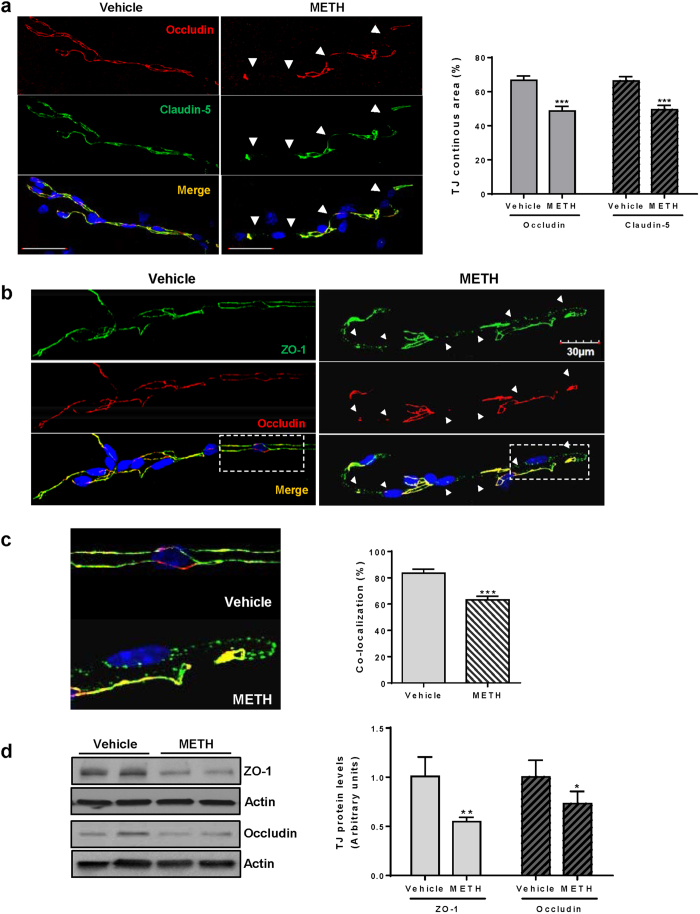
Figure 1. Chronic METH exposure alters TJ protein expression in brain microvessels.
(a) Mice were exposed to METH or vehicle control as described in the Methods, followed by immunostaining of microvessels for claudin-5 (green) and occludin (red). Images were taken with a confocal microscope. Arrow heads indicate areas where occludin or claudin-5 immunoreactivity was discontinued. These areas were measured, expressed as percent of the total microvessel surface, and illustrated in the form of a bar graph. (b) Microvessels were isolated as in (A) and immunostained for ZO-1 (green) and occludin (red). Arrow heads indicate the areas where occludin and ZO-1 immunoreactivity was reduced and these proteins were not co-localized. (c) Enlarged images from B (rectangles) show the details of fragmented ZO-1 and occludin immunoreactivity in microvessels from controls and METH-exposed mice. The co-localization area of occludin and ZO-1 immunoreactivity was measured, expressed as percent of the total microvessel surface, and illustrated in the form of a bar graph. (d) Immunoblotting analysis of protein expression of occludin and ZO-1 in the hippocampal homogenates 24 h after chronic METH administration. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***p < 0.0001 vs vehicle (n = 5 per group).