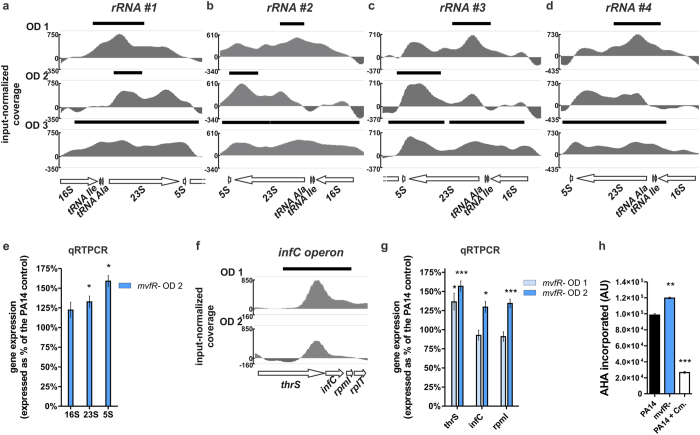
Figure 7. MvfR slows down translation activity by binding to and negatively regulating translation related genes.
(a–d,f) ChIPseq analysis reveals that MvfR binds to the 4 rRNA regions – rRNA #1 (a), rRNA #2 (b), rRNA #3 (c) and rRNA #4 (d) – as well as the infC operon (f). The black bar above the binding intensity plots represents the peak identified using SPP peak caller. (e,g) qRTPCR analysis indicates that MvfR represses the expression of 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs as well as thrS, infC, and rpmI. Faint blue bar = mvfR mutant at OD600nm 1, light blue bar = mvfR mutant at OD600nm 2. Data show the average +/− SEM of 3 independent replicates. Statistical significance was assessed using unpaired T test for rRNA genes and one way ANOVA + Dunnett’s post-test for infC operon genes. (h) MvfR inhibits the translation activity of P. aeruginosa as reflected by the measurement of newly synthetized proteins using the labeled amino-acid alanine AHA (L-azidohomoalanine). The translation inhibitor chloramphenicol (15 mg/L) was used as a control. Data show the average +/− SEM of three independent replicates. Statistical significance was assessed using one way ANOVA + Dunnett’s post-test.