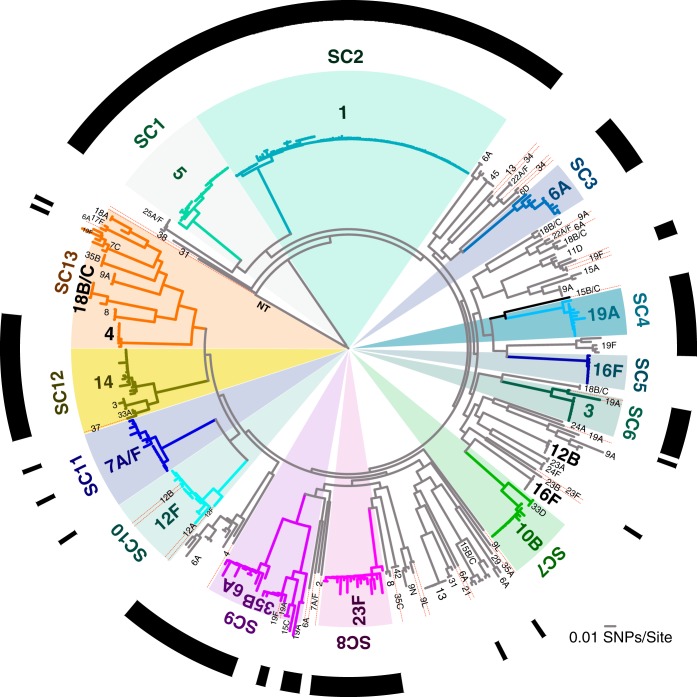
FIG 1 .
Population structure of S. pneumoniae strains from carriers and patients with invasive disease. The phylogeny was constructed using a 0.79-Mb multiple-sequence alignment with 51,389 SNPs from 852 universally conserved (core) genes present in single copies. The 14 sequence clusters (SCs) identified by BAPS are labeled on the edge of the phylogeny. Clades corresponding to the 13 different monophyletic SCs (SC1 to SC13) are shown in different colors, while clades for all the strains in the polyphyletic clade (SC14) comprising of the “unclustered” sequences are not colored. The outermost ring around the phylogeny shows whether a serotype is a vaccine type (VT) included in the PCV13 pneumococcal vaccine formulation (black) or nonvaccine type (NVT) not included (white). Phylogeny was rooted using an outgroup method on a branch containing nontypeable (NT) pneumococci, which are genetically distinct from all pneumococcal strains.