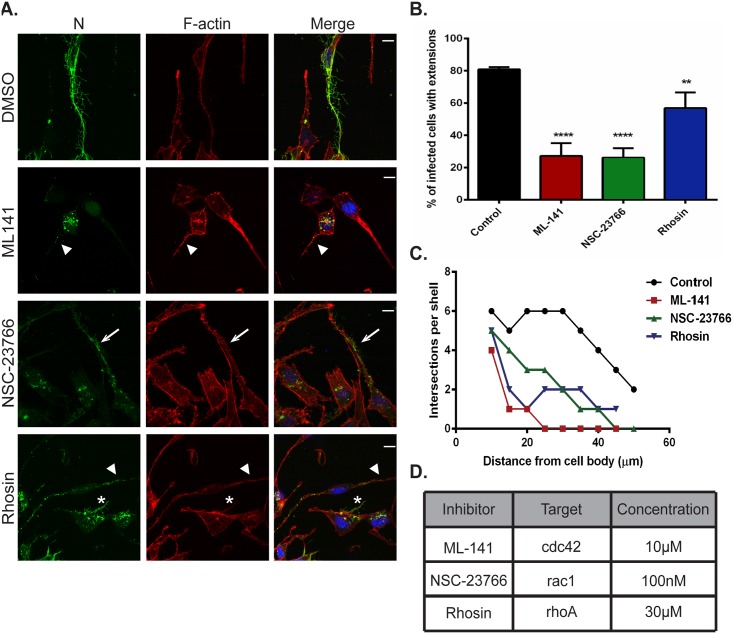
Fig 5. Rho GTPases Cdc42, Rac1 and RhoA contribute to formation of branched filamentous networks and intercellular extensions.
(A) BEAS-2B cells were inoculated with HMPV, and the indicated drug was added 2 hours later. Twenty-four h.p.i. cells were fixed and stained for HMPV N or F-actin. Arrows indicate an intercellular extension. Arrowheads show punctate localization of N, and asterisks indicate short branched filaments. (B) Images acquired from three independent experiments were processed, and a total of 100 infected cells were manually assessed for the presence of extensions. Data represents mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, (*** = p< 0.0001; ** = p< 0.001). (C) A total of 10 cells from three independent experiments were traced using the NeuronJ plugin of the ImageJ analysis tool and the degree of branching was evaluated using Sholl analysis. (D) Table showing the targets of the inhibitors used and their specific concentration.