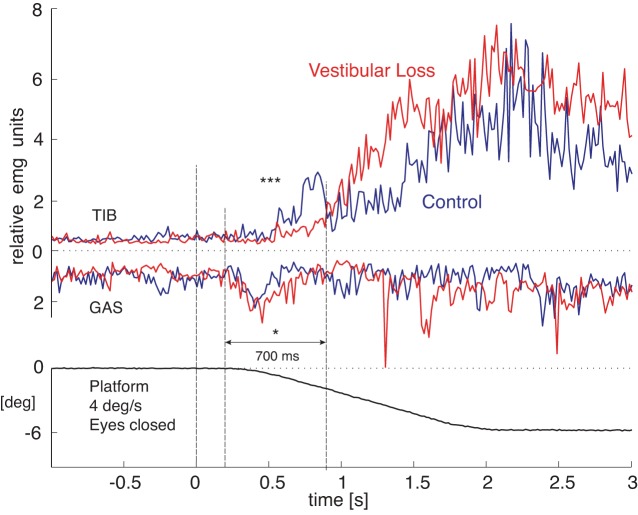
Fig. 7.
Group-averaged TIB and GAS electromyographic (EMG) activity in response to the 4 deg/s surface tilt resulting in a fall in subjects with vestibular loss and their eyes closed. The group of subjects with vestibular loss (red lines) showed significantly less TIB integrated EMG (IEMG) than the control group (black lines, ***P < 0.001) and significantly more GAS IEMG activity (*P < 0.05) during the initial postural response (200–900 ms after onset of surface tilt). Each subjects' contribution to the group average was from their mean of three responses. EMG integrals were normalized to the mean value 1 s prior to platform rotation onset to 1.5 s after platform onset to control for individual differences in EMG amplitudes.