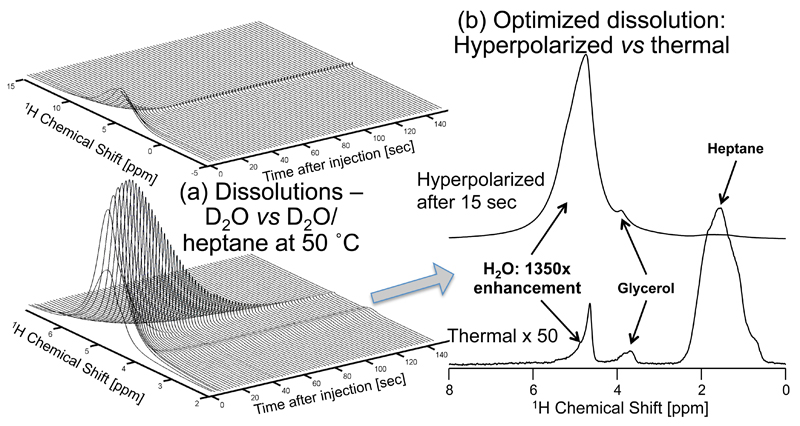
Figure 2.
Improving water’s hyperpolarized signal by co-dissolution with heptane. (a) Water signal evolution following hyperpolarization of a 150 µL 3:2 (v/v) mixture of H2O:Glycerol with 25 mM TEMPO, and dissolution in either 3 mL at ~35°C D2O (top), or in a mixture of 1.5 mL D2O and 3mL heptane with transport and measurement at ca. 50°C (bottom). The relaxation time T1 of the water resonance is extended from 3.6 sec (top) to 18.2 sec (bottom), and the absolute enhancement at t = 0 is increased by a factor of 4.5. (b) Comparison between the hyperpolarized 1D 1H NMR arising from the D2O/heptane dissolution 15 seconds after it has reached the NMR magnet, and a thermal spectrum of the same sample. All spectra were obtained by acquiring 28 k complex data points using a small (~1°) flip-angle pulse excitation and a carrier frequency set to 2.9 ppm; time zero corresponds to the conclusion of the sample flushing from the DNP polarizer.