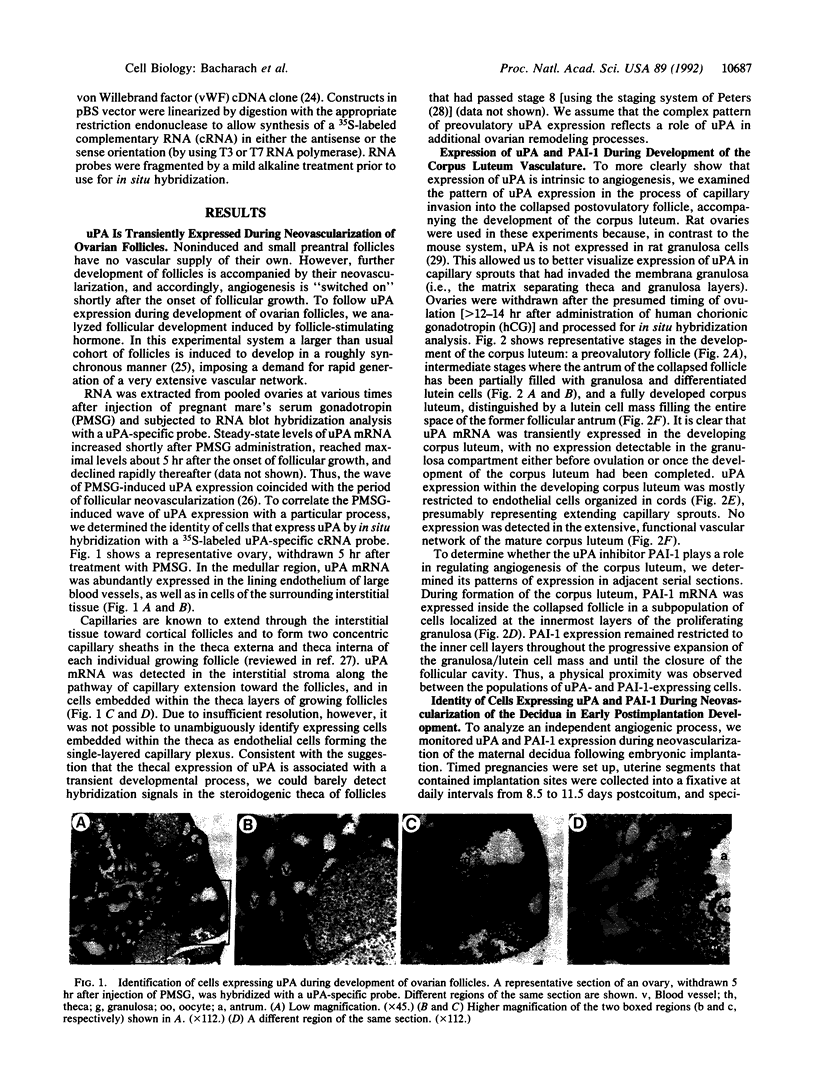
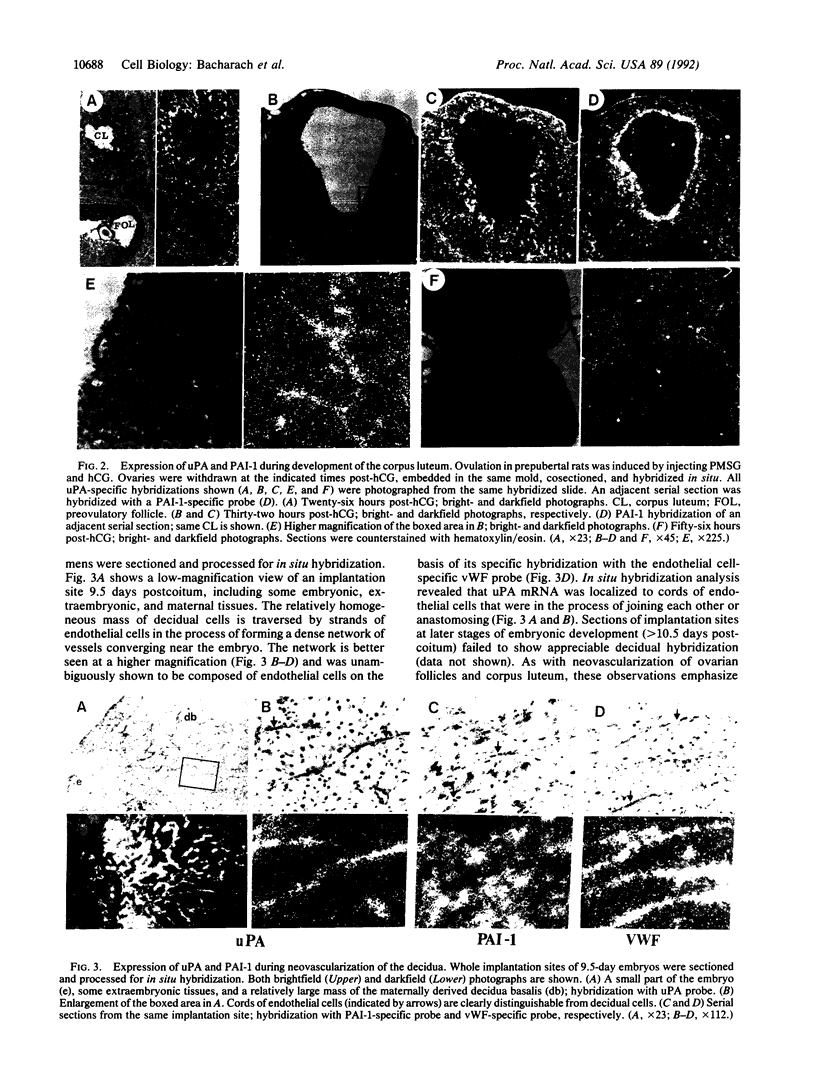
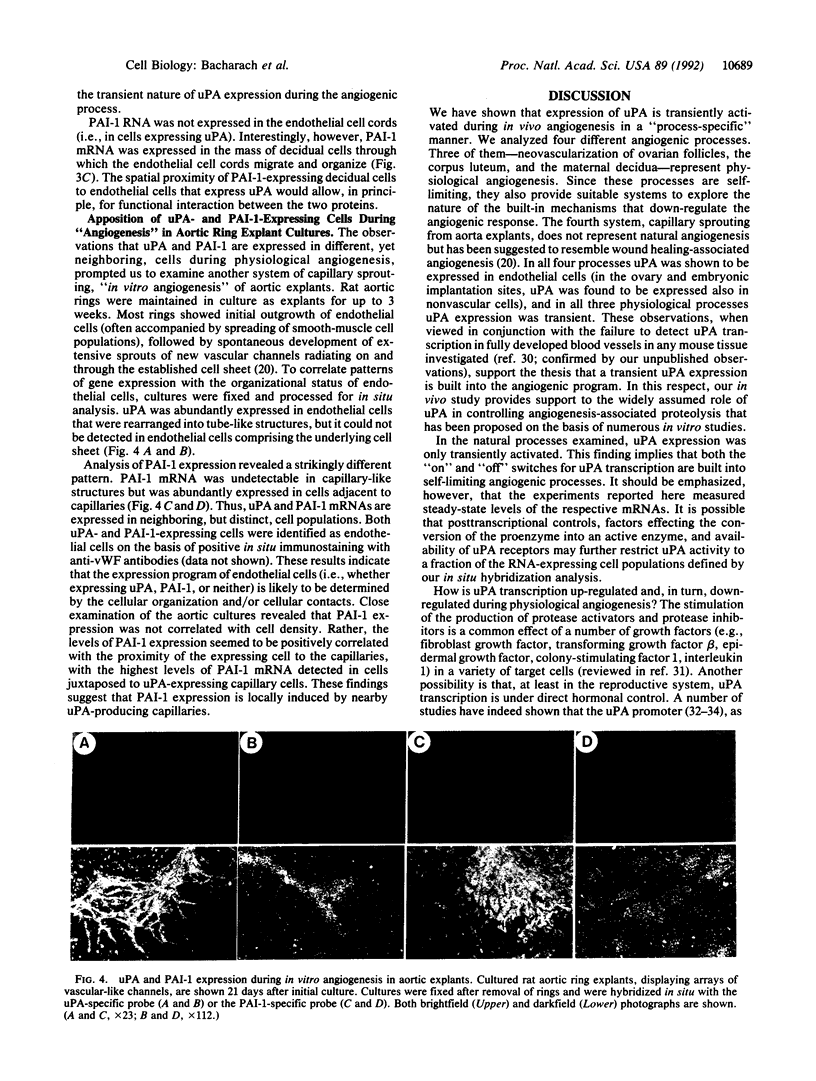
Abstract
To evaluate the role of plasminogen activators (PAs) in physiological angiogenesis, we have investigated the in vivo patterns of expression of urokinase-type PA (uPA) and PA-inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) during neovascularization of ovarian follicles, the corpus luteum, and the maternal decidua. Using in situ hybridization, we detected uPA mRNA in the ovary along the route of capillary extension, originating at the existing ovarian vasculature, extending toward growing follicles, and terminating at the newly formed capillary sheaths surrounding each growing follicle. Following ovulation, uPA mRNA was expressed in capillary sprouts within the developing corpus luteum. During the process of decidual neovascularization, uPA expression was detected in endothelial cell cords traversing the maternal decidua in the direction of the newly implanted embryo. uPA mRNA was not detected in endothelial cells upon completion of neovascularization, suggesting that uPA expression is a part of the angiogenic response. During in vitro "angiogenesis" of cultured aortic explants, uPA was expressed in capillary sprouts but not in underlying endothelial cell sheets, suggesting that the expression of uPA depends on the histological context of the endothelial cell. Interestingly, during corpus luteum development and decidual neovascularization, and in aortic explants, PAI-1 expression was preferentially activated in cells in the vicinity of uPA-expressing capillary-like structures. These findings suggest a functional interplay between uPA- and PAI-1-expressing cells and support the idea that natural PA inhibitors function during angiogenesis to protect neovascularized tissues from excessive proteolysis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Combépine C., Godeau F., Nagamine Y., Reich E., Kocher H. P., Duvoisin R. M. Cloning, nucleotide sequencing and expression of cDNAs encoding mouse urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Nucleotide sequence of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7125–7127. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cajot J. F., Bamat J., Bergonzelli G. E., Kruithof E. K., Medcalf R. L., Testuz J., Sordat B. Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 is a potent natural inhibitor of extracellular matrix degradation by fibrosarcoma and colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canipari R., O'Connell M. L., Meyer G., Strickland S. Mouse ovarian granulosa cells produce urokinase-type plasminogen activator, whereas the corresponding rat cells produce tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):977–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diglio C. A., Grammas P., Giacomelli F., Wiener J. Angiogenesis in rat aorta ring explant cultures. Lab Invest. 1989 Apr;60(4):523–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. K. Angiogenesis in reproductive tissues. J Endocrinol. 1986 Dec;111(3):357–366. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1110357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Lucore C. L., Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J., Sobel B. E. Induction of synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 by tissue-type plasminogen activator in human hepatic and endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Nov 30;64(3):412–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. Increased capillary endothelial cell protease activity in response to angiogenic stimuli in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter P., Kikinis Z., Altus M. S., Pearson D., Nagamine Y. A new genetic approach for studying hormonal regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in LLC-PK1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4535–4541. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert C. A., Baker J. B. Linkage of extracellular plasminogen activator to the fibroblast cytoskeleton: colocalization of cell surface urokinase with vinculin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1241–1247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalebic T., Garbisa S., Glaser B., Liotta L. A. Basement membrane collagen: degradation by migrating endothelial cells. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):281–283. doi: 10.1126/science.6190230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):341–349. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1899685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Santell L. Association of a plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) with the growth substratum and membrane of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2543–2549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F. Enzyme systems. Better reception for urokinase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):488–489. doi: 10.1038/344488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Schleef R. R., Loskutoff D. J. Extracellular matrix of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells contains functionally active type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):721–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Pepper M. S., Möhle-Steinlein U., Risau W., Wagner E. F., Orci L. Increased proteolytic activity is responsible for the aberrant morphogenetic behavior of endothelial cells expressing the middle T oncogene. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Orci L. Phorbol ester induces cultured endothelial cells to invade a fibrin matrix in the presence of fibrinolytic inhibitors. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):509–516. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Baird A., Guillemin R., Orci L. Basic fibroblast growth factor induces angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses M. A., Sudhalter J., Langer R. Identification of an inhibitor of neovascularization from cartilage. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.1694043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro B., Itin A., Sachs L., Keshet E. Pattern of interleukin 6 gene expression in vivo suggests a role for this cytokine in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Montesano R., Orci L. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is induced in migrating capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2535–2541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Travis J., Punsal P. I. Elastase regulates the synthesis of its inhibitor, alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor, and exaggerates the defect in homozygous PiZZ alpha 1 PI deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1774–1780. doi: 10.1172/JCI113519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. The development of the mouse ovary from birth to maturity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 Sep;62(1):98–116. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0620098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Hedman K., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Vaheri A. Ultrastructural localization of plasma membrane-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator at focal contacts. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):87–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. S. Maturation of ovarian follicles: actions and interactions of pituitary and ovarian hormones on follicular cell differentiation. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):51–89. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Grimaldi P., Blasi F., Geremia R., Verde P. Follicle-stimulating hormone and cyclic AMP induce transcription from the human urokinase promoter in primary cultures of mouse Sertoli cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):940–946. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Leung A. Glucocorticoids stimulate plasminogen activator production by rat granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):1595–1601. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Curriden S. A., Loskutoff D. J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene: functional analysis and glucocorticoid regulation of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]