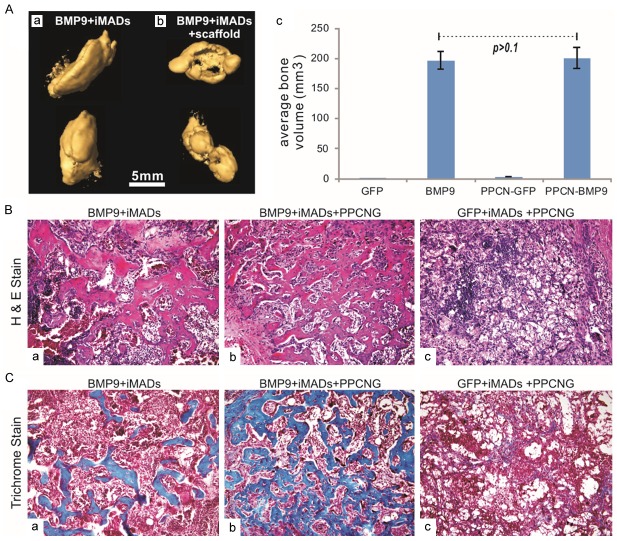
Figure 6.
BMP9 induces robust ectopic bone formation from the iMADs implanted with scaffold materials. (A) Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP for 30 h, and implanted into athymic nude mice subcutaneously either by direct cell injection or mixing with thermoresponsive biodegradable scaffold material PPCN-gelatin (5x106 cells per injection, n=5 per group). After 4 weeks, the subcutaneous masses at the injection sites were collected and fixed for microCT imaging (a & b). Average bone volumes were calculated using Amira software (c). No masses were retrieved from the group injected with Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells only, nor were bony masses recovered from the group injected with Ad-GFP infected iMADs mixed with PPCN-gelatin scaffold material. (B) H&E staining of the masses retrieved from subcutaneous injection with Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cell only (a), Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (b) or Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (c). Representative images are shown. (C) Trichrome staining of the masses retrieved from subcutaneous injection with Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cell only (a), Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (b) or Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (c). Representative images are shown.