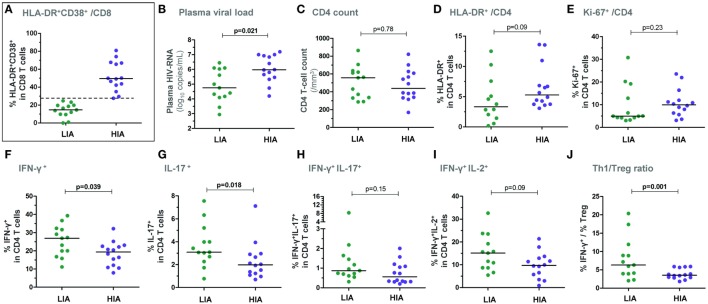
Figure 1.
Patients with higher levels of CD8 T-cell activation show lower ex vivo CD4 T-cell responsiveness in early PHI. Patients were segregated based on the level of ex vivo CD8 T-cell activation at baseline: the group with higher immune activation (HIA) was defined as % HLA-DR+CD38+ CD8 T cells ≥ median and the group with lower immune activation (LIA) as % HLA-DR+CD38+ CD8 T cells < median (A). Plasma viral load (B), CD4 T-cell counts (C), % HLA-DR+ CD4 T cells (D), and % Ki-67+ CD4 T cells (E) are depicted in both patient groups. Freshly isolated CD4 T cells (at baseline) were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 5 h and frequencies of IFN-γ+ (F), IL-17+ (G), IFN-γ+IL-17+ (H), as well as of IFN-γ+IL-2+ (I) CD4 T cells are shown in HIA and LIA patients. The ratios between effector Th1 responses (% IFN-γ+) and ex vivo CD25+CD127lowFoxP3+ regulatory T cells are also depicted (J). P-values of Mann–Whitney tests are indicated on each panel.