Figure 7.
Analysis of the PI 3-Kinase-AKT Signaling Pathway in CTL
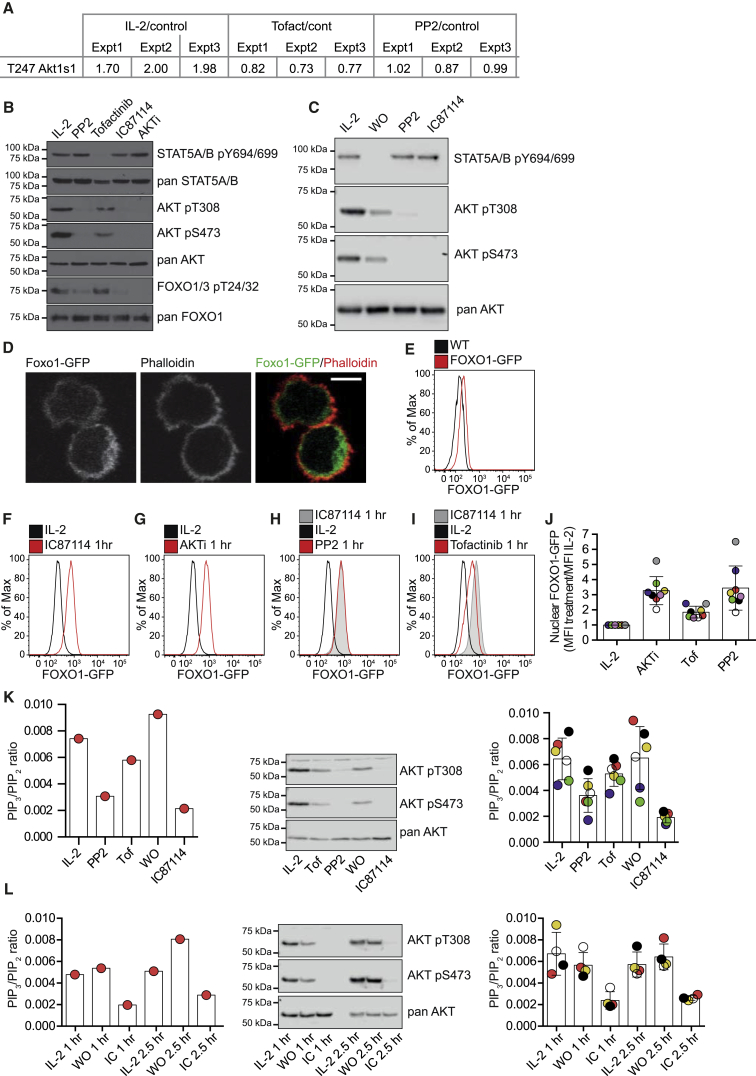
(A) The regulation of PRAS40/AKT1S1 in CTLs as determined by SILAC phosphoproteomics.
(B and C) Immunoblot analysis of AKT phosphorylation in CTLs maintained in IL-2 alone and treated for 1 hr with 10 μM PP2, 100 nM Tofacitinib, 10 μM IC87114, a PI3K-p110δ inhibitor, or 1 μM AKTi, an AKT inhibitor (B) and in response to 1 hr IL-2 deprivation (C).
(D–J) IL-2-maintained CTLs were generated from FOXO1-GFP mice. The localization of FOXO1-GFP (green) was visualized by microscopy (D), with the actin cytoskeleton detected using phalloidin (red). The scale bar is 5 μm. FOXO1-GFP levels in nuclear extracts of IL-2-maintained CTLs were quantified by flow cytometry under basal conditions (IL-2) and compared to a non-FOXO1-GFP-expressing CTL (WT) (E) or following 1 hr treatment with IC87114 (F), AKTi (G), PP2 (H), or Tofacitinib (Tof) (I). Representative flow cytometry profiles are shown in (F–I), with the level of FOXO1-GFP in each condition expressed as a ratio of the MFI of the IL-2 control of eight color-matched biological replicate treatments shown in (J), with bars showing the mean ± SD.
(K and L) The levels of PIP3 in CTLs maintained in IL-2 only, shown as a ratio of the measured PIP2, were determined using mass spectrometry. In (K), IL-2-maintained CTLs were treated with 100 nM Tofacitinib (Tof), 10 μM PP2, 10 μM IC87114, or deprived of IL-2 (WO) for 30 min and compared to IL-2-maintained CTL control cells. In (L), PIP3 levels were measured in CTL maintained in medium alone (WO) and were compared to control (IL-2) and IL-2 + IC87114-treated cells for up to 2.5 hr. In (K) and (L), the left-hand panels show the data for a single experiment, with the immunoblot analysis of the phosphorylation of AKT on pT308 and pS473 shown in the middle panel. The right panel shows the results for color-matched biological replicates, 6 in (K) and 4 in (L). Bars show the mean ± SD.