FIGURE 2.
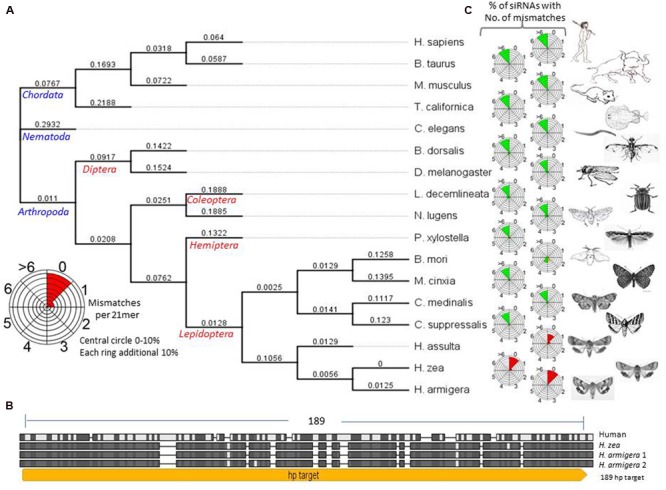
(A) Acetylcholinesterase (ACE) phylogenetic tree based on nucleic acid sequences made with the neighbor-joining method. Bombyx mori (B. mori; DQ115792), Bos taurus (B. Taurus; NM_001076220), Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans; X75331), Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster; X05893), Helicoverpa armigera (H. armiger; AF369793), Helicoverpa assulta (H. assulta; AY817736), Helicoverpa zea (Supplementary Figure S1), Homo sapiens (H. sapiens; M55040), Leptinotarsa decemlineata (L. decemlineata; L41180), Mus musculus (M. musculus; X56518), Nilaparvata lugens (N. Lugens; AJ852420), Torpedo californica (T. californica; X03439), Chilo suppressalis (C. supressalis; EF470245.1), Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (C. medinalis; FN538987.1), Melitaea cinxia (M. cinxia; GQ489250.1), Plutella xylostella (P. xylostella; AY032625.1). (B) H. armigera ACE nucleotide sequence showing the hairpin target site, alignment of ACE1 nucleotide sequences from H. sapiens, H. zea, H. armigera and ACE2 of H. armigera. Conserved residues are enclosed in black/gray boxes, hairpin target region indicated in yellow (hp189). See Supplementary Figure S1 for details of sequence. (C) Radial siRNA relationship icons for each species calculated by TK-siRNA software at benthgenome.com. They indicate the percentage of possible siRNAs from the H. armigera ACE hpRNA sequence that have 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or >6 mismatches with the corresponding gene in the different species. Twenty-one nucleotides of siRNA sequences with 0, 1, or 2 mismatches are expected to target cleavage of the target gene (and shown in red), those with >3 mismatches are shown in green and expected to have no significant RNAi effect. Those shown in orange are placed in the category of possibly having an RNAi effect. Each successive circle represents a 10% bin from 0–10 to 90–100%. For example: a completely red sector for 0 mismatches (e.g., for H. armigera) represents 100% of the potential siRNAs are predicted to direct an RNAi effect and a completely green sector for >6 mismatches (e.g., for H. sapiens) represents 100% of the potential siRNAs are predicted to not direct an RNAi effect. The prediction about degrees of mismatch having an RNAi effect comes from the results shown in Supplementary Figure S2.
