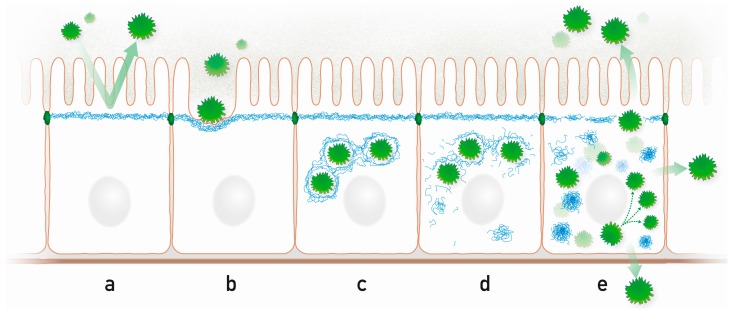
Figure 2.
Highly schematic representation of processes that may occur during microbe-intermediate filament interaction in a simple epithelium. (a) The subapically enriched cytoplasmic IF system acts as an intracellular protective barrier; (b) IFs form together with the actin cytoskeleton pedestals for attached microbes; (c) Intracellular microbes are encaged by IFs; (d) Microbes disrupt the IF cage through kinase activities, which modify IF polypeptides and initiate the formation of cytoplasmic IF aggregates; (e) Released microbes proliferate and spread to neighboring cells and to the environment disrupting the protective apical IF network. Prominent cytoplasmic aggregates containing hyperphosphorylated IFs appear.