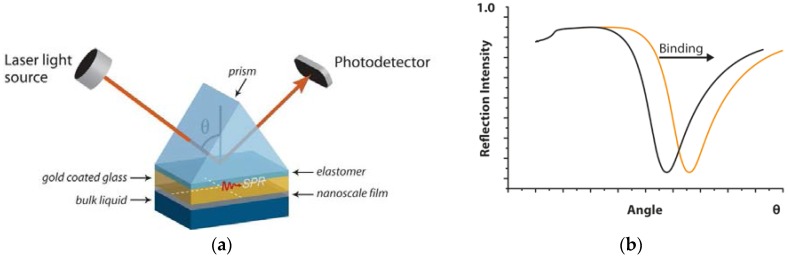
Figure 1.
(a) measurements are performed on a sensor slide, typically a gold-coated glass slide that is placed between the prism and flow-cell. Multi-Parametric Surface Plasmon Resonance (MP-SPR) consists of an incident beam of p-polarized light that strikes electrically, and conducting sensors slide at the interface with high refractive index and an external medium (gas or liquid) with low refractive index. The incident beam jet moves at different angles and the determinate angle where surface plasmons exits take place, resulting in a reduced intensity of the reflected light and indicating changes in SPR signal due to surface molecular interactions; (b) the graph shows a shift in SPR due to formation of a layer at the surface. The x-axis is the angle at which the laser excites plasmons. The y-axis shows the level of light intensity reflected from the surface. The dip in the curve (lowest light intensity) shows when the plasmons are excited.