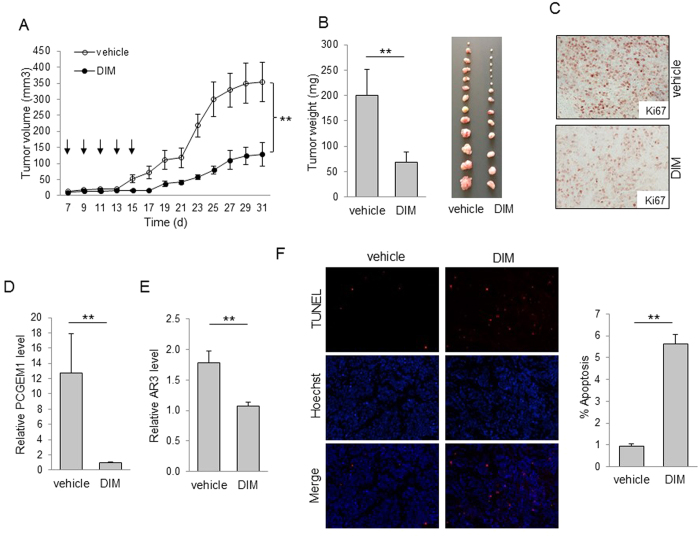
Figure 6. DIM reduces prostate tumor growth by suppression of PCGEM1 in the castrated xenograft mouse model.
(A) Effect of DIM on tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Male SCID mice were first castrated and one week later, CWR22Rv1 cells were injected into flanks as described in the materials and methods. Arrows indicate DIM administration. Tumor growth was measured every other day after 7 days of injection. (B) Tumors were harvested at day 31 and weighed. Actual tumor size after harvest was shown in the right panel. (C) DIM suppresses Ki-67 signal. The excised tumors were formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded, and stained with Ki-67 antibody. (D) DIM suppresses PCGEM1 and (E) AR3 in xenograft tumors. RNA was extracted from three individual tumors. (F) DIM induces apoptosis in tumors as determined by TUNEL assays. Apoptotic cells were counted in 10 random fields per group under a fluorescent microscope (×20 magnification). Values in D and E are mean ± SE (n = 3). **p < 0.01.