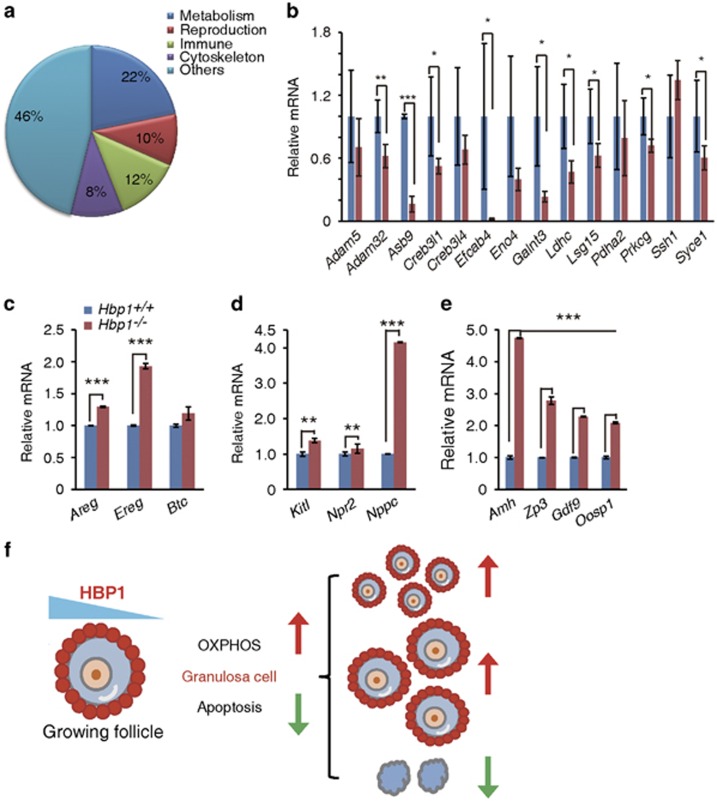
Figure 7.
Microarray results of global transcriptional changes and quantitative PCR analysis of metabolic or primordial follicle dormancy-related genes in Hbp1-deficient mice. (a) Functional classification of the microarray data for the most significantly changed genes in the ovaries of Hbp1−/− versus wild-type mice of P21. The percentage of genes sharing common biological processes is shown. (b) Q-PCR confirmation of metabolic genes showing significant changes in microarray analysis in ovary. Relative mRNA values are normalized to Rpl19, and the data are presented as the mean values±S.D. of three independent experiments. (c–e) Q-PCR results of EGF ligand family genes (Areg, Ereg and Btc) that are essential for increased follicle survival, oocyte and primordial follicle dormancy marker genes (Amh,Zp3,Gdf9 and Oosp1), and the genes (Kitl, Npr2 and Nppc) essential for communication between oocytes and GCs in the ovaries of 2-month-old mice. Relative mRNA values are normalized to Rpl19, and the data are presented as the mean values±S.D. of three independent experiments. (f) Model of dose-dependent HBP1 determines the mitochondrial function and therefore contributes to follicle survival and increased ovarian reserve