Fig. 3.
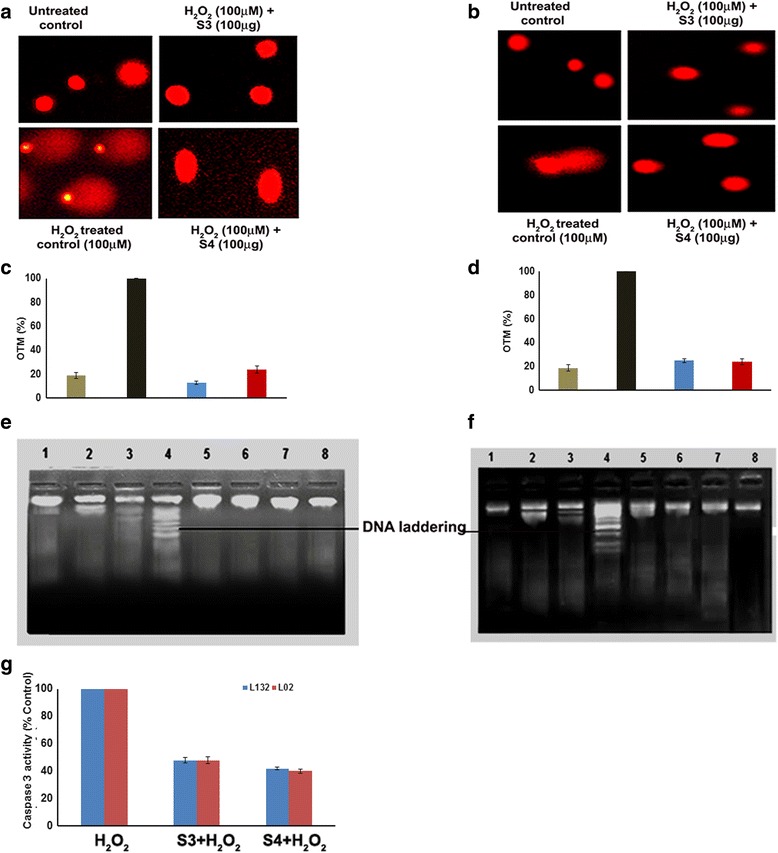
Protective effect of 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol on H2O2 induced cell death. Lung (a) and liver (b) cells were pretreated with 100 μg of isolated 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol separately followed by H2O2 (100 μM) and DNA damage was observed using fluorescence microscopy. Olive tail movement of DNA in lung (c) and liver cells (d) calculated using image pro plus software. Cells not treated with H2O2 were served as untreated control and only H2O2 treated cells were served as a control. Lung (e) and liver (f) cells pretreated with isolated 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol (100 μg) followed UV or H2O2 (100 μM) alone or UV and H2O2 (100 μM). DNA isolated and electrophoresed to observe the band pattern. Lane (1) indicates the DNA of untreated cells, Lane (2) and (3) indicates DNA of UV and H2O2 treated cells, respectively. Lane (4) indicates the DNA of UV and H2O2 treated cells. Lane (5) and (6) indicates to the DNA of pre-treated cells with isolated 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol at concentration of 100 μg, respectively H2O2 Lane (7) and (8) indicates the DNA of cells treated with isolated 3-O-methyl quercetin (S3) and kaempferol (S4) alone at 100 μg concentration. Effect of isolated 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol (100 μg) on caspase 3 activity (g). Each value represents mean ± SE of three independent experiments. The values were significant at p < 0.05
