Fig. 2.
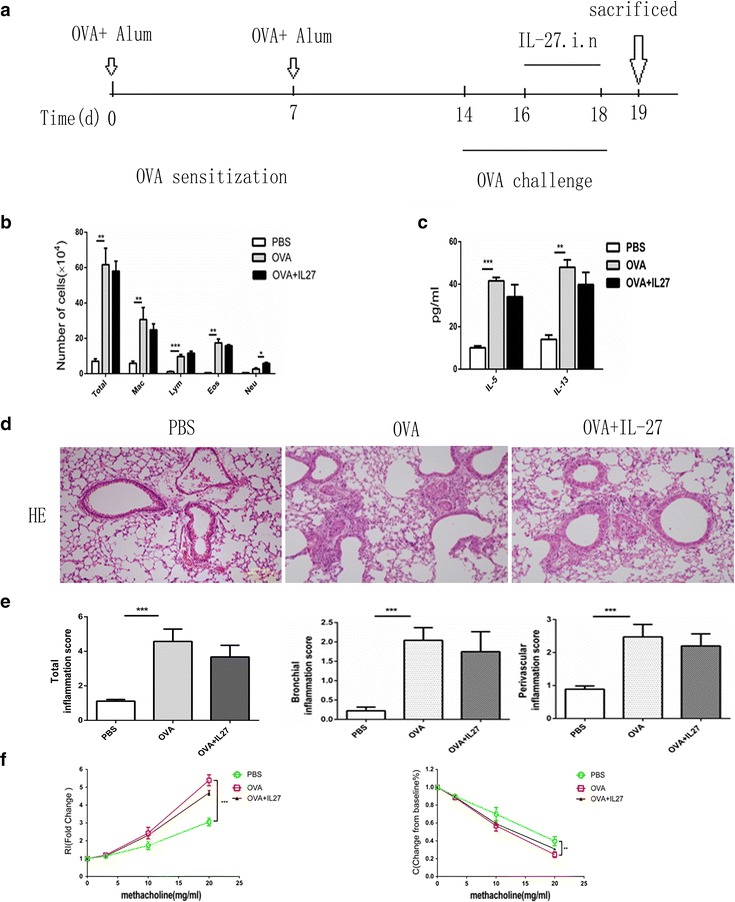
Therapeutic intranasal administration of IL-27 does not result in significant improvement of airway inflammation in an OVA-induced mouse model. a Protocol of OVA-induced allergic asthma and IL-27 administration. b The total cell number and the differential cell counts in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). The total cell number and the differential cell counts had no significant difference in IL-27 treated group. c The concentrations of Th2 cytokines in BALF were measured by ELISA. IL-5 and IL-13 level was not markedly changed in IL-27 treated group. d Representative photomicrographs of lung sections stained with H&E were examined. There was no improvement of inflammation around airway and vessels in IL-27 treated group. e The inflammation scores of peribronchial and perivascular inflammation cells didn’t decreased in IL-27 treated group. f AHR was measured by invasive measurement of lung resistance in response to increasing concentrations of methacholine. IL-27 treatment had no improvement in lung resistance. The columns and error bars represent the mean and SEM (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Similar results were obtained in at least six independent experiments
