Fig. 4.
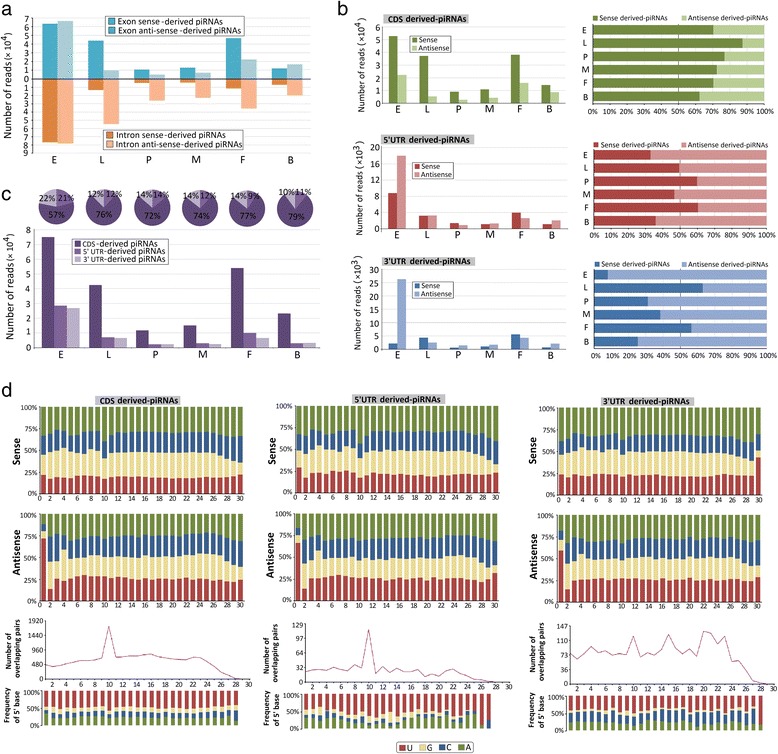
Characterization of gene-derived piRNAs. a Abundances and strand preference of exon-derived and intron-derived piRNAs from six developmental stages. b Abundance and percentage of CDSs, 5′ UTR- and 3′ UTR-derived piRNAs. c Abundance and strand preference of CDS-derived reads, 5′ UTR-derived reads and 3′ UTR-derived reads from six developmental stages of the Ae. albopictus dataset. d Upper panel: Base composition of CDSs, 5′ UTR- and 3′ UTR-derived piRNAs. The X-axis represents the nucleotide position relative to the 5′ ends of the piRNAs. The Y-axis represents the percentage of base bias. Lower pane: ping-pong pair analysis of CDSs, 5′ UTR- and 3′ UTR-derived piRNAs. The length of overlap is shown on the horizontal axes. Indicated above each axis is the number of possible overlapping pairs of small RNAs with a specified overlap size. Indicated below each axis is the relative frequency of the 5′ base identity for overlapping sequences. The colour code for bases is indicated in the centre box
