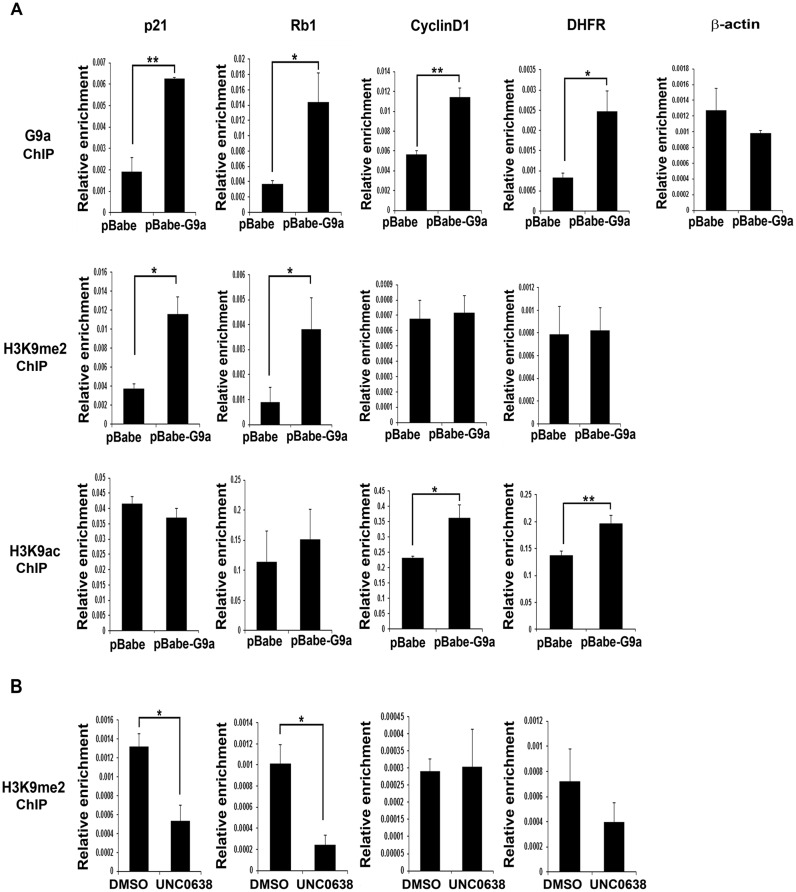
Figure 4.
G9a mediates H3K9me2 on cell cycle exit genes but not on E2F1 target genes. (A) G9a occupancy, H3K9me2 and H3K9ac marks were analysed by ChIP assays at p21, Rb1, CyclinD1, DHFR and β-actin promoters in pBabe and pBabe-G9a cells cultured in growth medium. G9a occupancy was increased in G9a overexpressing cells at all these promoters except β-actin, which was used as a negative control. H3K9me2 enrichment was apparent at the p21 and Rb1 promoters in pBabe-G9a cells, but not at CyclinD1 and DHFR promoters. In contrast, H3K9ac was seen at CyclinD1 and DHFR promoters but not at p21 and Rb1 promoters. The results are representative of two independent experiments. Error bars indicate the mean of qRT-PCT triplicates in each experiment ± SD. (B) p21, Rb1, CyclinD1 and DHFR promoters were analysed for H3K9me2 in C2C12 cells treated with either DMSO or UNC0638 for 48 hr in growth medium. UNC0638 treatment reduced H3K9me2 at p21 and Rb1 promoters, but did not impact this mark at CyclinD1 and DHFR promoters. The results are representative of two independent experiments. Error bars indicate the mean of qRT-PCR triplicates in each experiment ± SD.