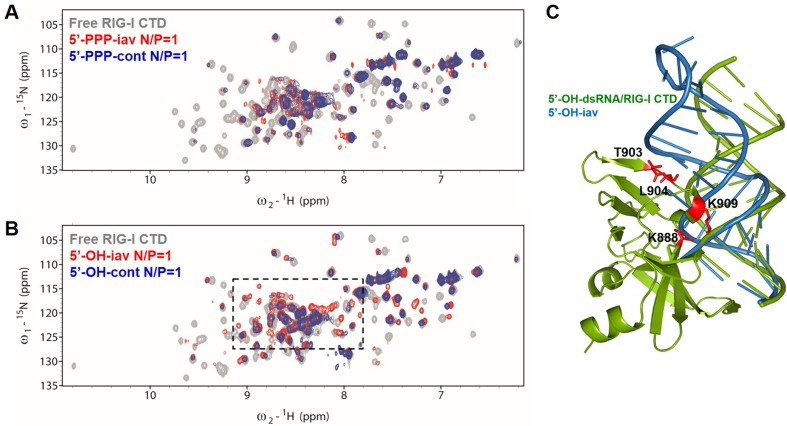
Figure 4.
NMR titration of 15N-labeled RIG-I CTD with iav RNAs and cont RNAs. (A) 15N-1H-HSQC spectra of free RIG-I CTD, 5′-PPP-iav/RIG-I CTD complex and 5′-PPP-cont/RIG-I CTD complex (gray, free protein; red, 1:1 complex with 5′-PPP-iav; blue, 1:1 complex with 5′-PPP-cont). N/P indicates RNA-to-Protein molar ratio. (B) 15N-1H-HSQC spectra of free RIG-I CTD, 5′-OH-cont/RIG-I CTD complex, and 5′-OH-iav/RIG-I CTD complex (gray, free protein; red, 1:1 complex with 5′-OH-iav; blue, 1:1 complex with 5′-OH-cont). Amide protons in the dotted boxes revealed dramatic changes in chemical shift upon RIG-I CTD binding to 5′-OH-iav. (C) Model of 5′-OH-iav/RIG-I CTD complex structure. Structure of iav RNA (blue, PDB 1JO7) was superimposed on 5′-OH-14bp-GC-dsRNA/RIG-I CTD complex (green, PDB 3OG8). Mutations at RIG-I CTD (K888, T903, L904 and K909) are indicated in red.