Fig. 3.
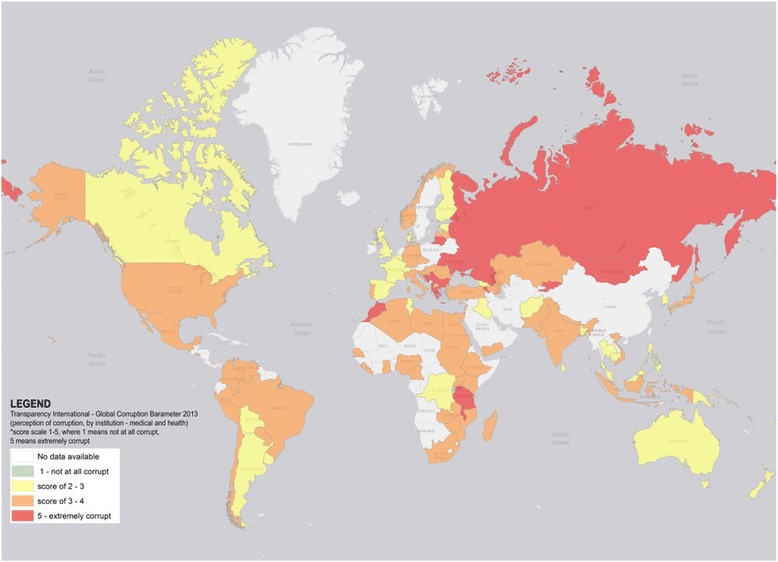
Heat map of Transparency International’s Global Corruption Barometer (GCB): perceptions of the extent of corruption in medical and health services institutions. Transparency International’s 2013 GCB uses surveys from more than 114,000 respondents in 107 different countries to assess people’s direct experiences and views on corruption in main institutions in their countries. This includes assessing perception of the extent of corruption in Medical and Health Services institutions measured on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 indicates “not at all corrupt” and 5 indicates “extremely corrupt.” The above map was generated using publicly available data from GCB and was visualized in ArcGIS map. It depicts the varying levels of public perception on how corrupt medical and health institutions are within respective countries (global mean score of 3.3)
