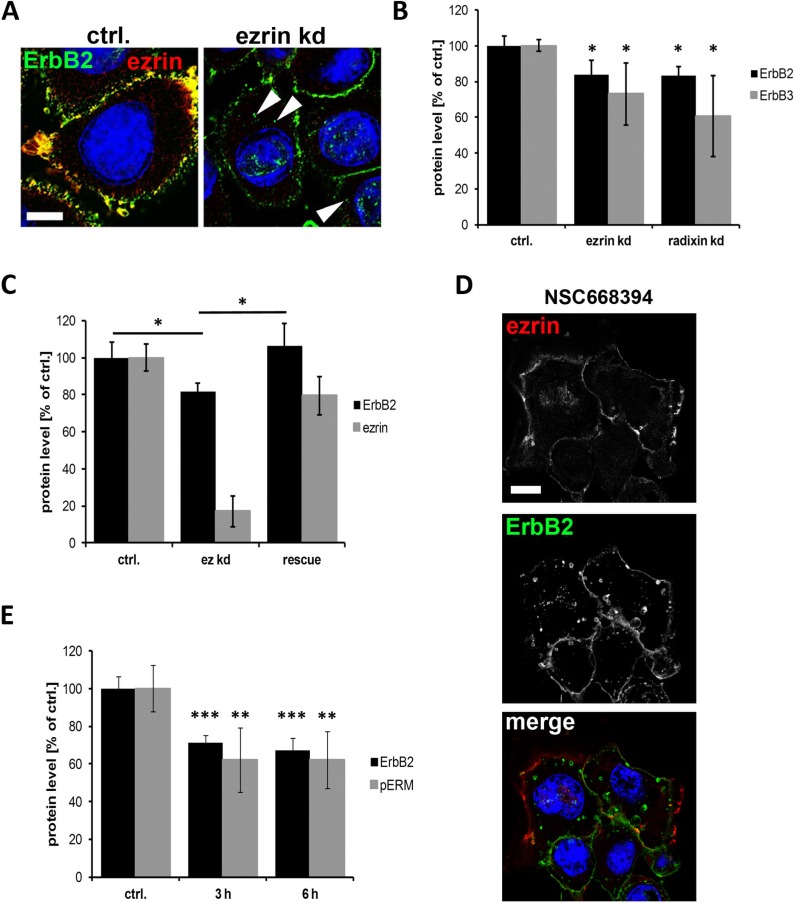
Figure 2. Internalization and degradation of ErbB receptors after interference with ERM proteins.
(A) Localization of ErbB2 in control and ezrin depleted SKBR3 cells. As observed by confocal microscopy (single plane section), ezrin depletion leads to localization of ErbB2 in intracellular vesicles (arrowheads). Scale bars: 10 μm. (B) Quantification of Western blot analysis of ErbB2 and ErbB3 protein levels after ERM knockdown. Depletion of ezrin or radixin leads to significantly reduced protein levels of ErbB2 and ErbB3. (C) ErbB2 protein level after rescue of ezrin levels. Cells rescued for ezrin levels by transfection of a siRNA resistant ezrin DNA upon ezrin knockdown, leads to restored protein levels of ErbB2. (D) Confocal microscopy (single plane section) of ErbB2 localization. Inactivation of ERM proteins by NSC668395 (3 h) leads to internalization of ErbB2 into vesicular structures. Scale bars: 10 μm. (E) Quantification of Western blot analysis of ErbB2 and pERM levels after treatment with NSC668394 for 3 h and 6 h. All data in this Figure represented as mean +/− SEM (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).