Figure 3. ERK2-directed phosphorylation contributes EBNA1-dependent transcriptional activity.
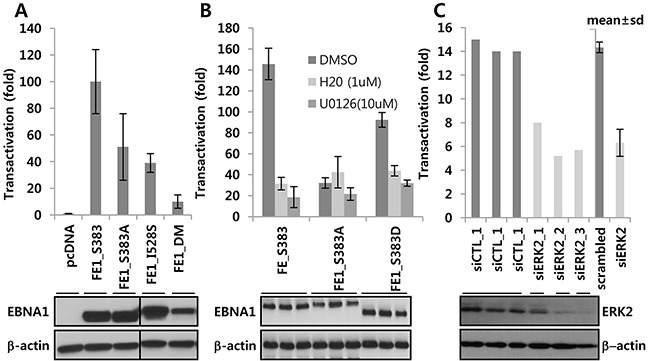
A. EBNA1-negative BJAB cells were transiently co-transfected with a control vector, EBNA1 S383, S383A, S528, and PAS, along with EBNA1-dependent (POLP2) and -independent (SV40p-RL) reporters. B. After transient co-transfection of indicated expression plasmids with reporters (see above), cells were divided into three aliquots, and treated with ERKi in the absence or presence of DMSO, H20 (0.5 μM), and U0126 (10 μM). Slight difference in EBNA1 protein size resulted from variations in glycine-alanine (GA) repeats during PCR, as can be seen from Western blots underneath. C. Use of scramble siRNA or three different siRNAs against ERK2 (siERK2_1, _2, _3) resulted in partial knockdown 3 days post transfection of BJ-FE1 cells. These and control (siCTL) cells were transiently transfected with POLP2 and SV40p-RL reporters and assayed after 2 days. Note that the lower transactivation (~15 fold) is due to use of a stable BJAB cell line constitutively expressing FE1, which is usually lower than transiently transfected FE1.
