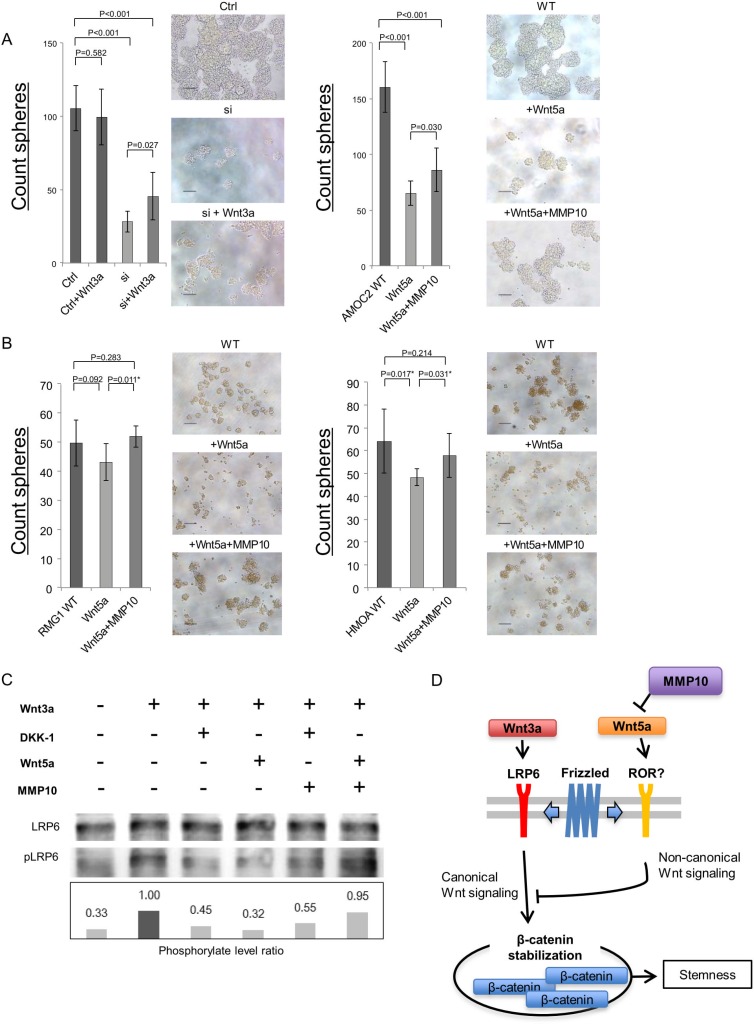
Figure 7. MMP10 activate canonical Wnt signaling by inhibition of noncanonical Wnt signaling ligand Wnt5a.
(A) Caninical Wnt signaling ligand Wnt3a increase the sphere-forming. A canonical Wnt signaling ligand Wnt3a was added to AMOC2 cells that are transfected with control siRNA and MMP10 siRNA. A noncanonical Wnt signaling ligand Wnt5a and MMP10 were added. The numbers of spheres are shown. The numbers of Data are shown as means ± SD. (B) MMP10 cancel the inhibition of sphere-formation by Wnt5a. A noncanonical Wnt signaling ligand Wnt5a and MMP10 were added. The numbers of spheres are shown. The numbers of Data are shown as means ± SD. (C) A Western blot of canonical signaling. Total LRP6 protein and phosphorylated LRP6 (pLRP6) were detected by a Western blot. The intensity of bands were analyzed by imageJ software, and the phosphorylation levels of LRP6 were calculated as: intensity of phosphorylated LRP6/intensity of total LRP6. AMOC2 cells were incubated in medium containing Wnt3a, DKK1, Wnt5a and MMP10. (D) Schematic model of MMP10 in ovarian CSCs/CICs. A canonical Wnt ligand Wnt3a activate canonical Wnt signaling by activation of LRP6. A noncanonical Wnt lignad Wnt5a inhibit canonical Wnt signaling through an unknown receptor. MMP10 inhibit Wnt5a and increase the canonical Wnt signaling and following activation of β-Catenin that induce transcriptions of stem cell-related genes including SOX2, Oct3/4 and Nanog.