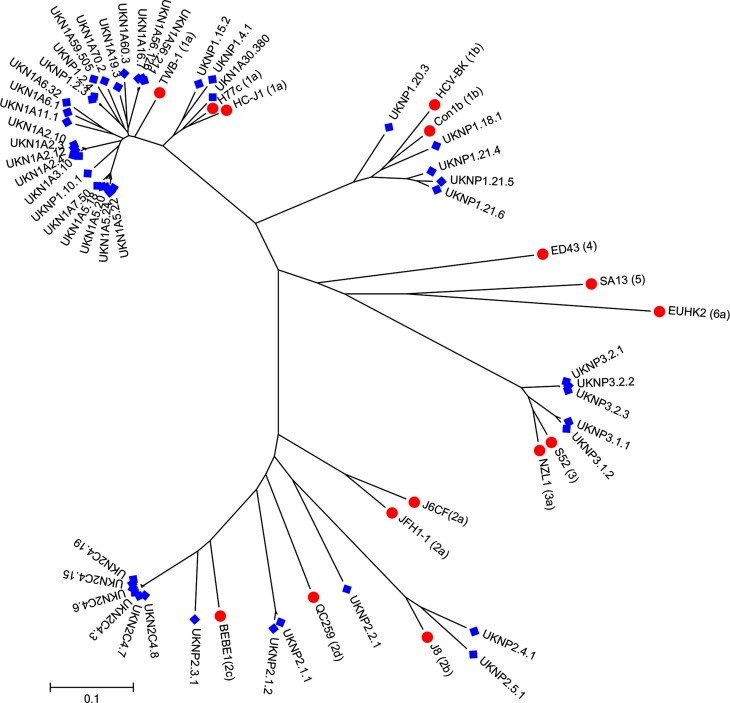
Fig. 3.
Maximum likelihood molecular phylogenetic analysis of HCV E1/E2 nucleotide sequences. The evolutionary history of the patient-isolated HCV E1/E2 genes cloned into chimeric HCVcc was inferred by using the maximum likelihood method based on the general time reversible model. The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying neighbour-joining and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the maximum composite likelihood approach, and then selecting the topology with superior log likelihood value. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 49 E1/E2 gene sequences (blue diamond) derived from 25 individual patients, and 15 genotype reference nucleotide sequences (red circle). Codon positions included were 1st + 2nd + 3rd + non-coding. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 1649 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in mega7 (Kumar et al., 2016).