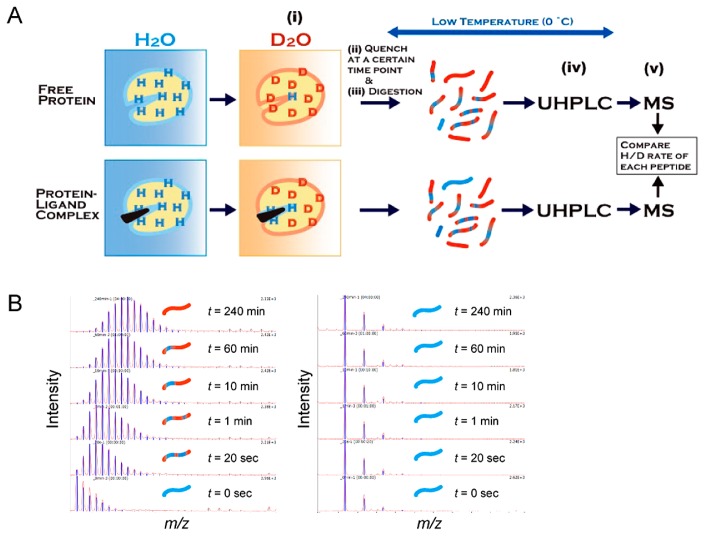
Figure 7.
Schematic presentation of hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS). (A) An experimental flowchart of HDX-MS for protein–ligand interactions. (i) A free protein or protein–ligand complex is placed into deuterium buffer to start the exchange reaction, (ii) the exchange reaction is quenched by lowering the pH and temperature, (iii) the protein is digested into peptides through the pepsin-immobilized column, (iv) the peptide fragments are separated by ultra-high performance reverse-phase liquid chromatography (UHPLC), and (v) the separated peptides are analyzed by MS and MS/MS. (B) Amide hydrogen in a peptide that is exposed to solvent and not involved in the secondary formation is rapidly exchanged with deuterium, leading to a mass increase by the H/D exchange reaction (left), while peptides located at the site of protein–ligand interaction show slow or no exchange during the observation period (right).