Figure 1.
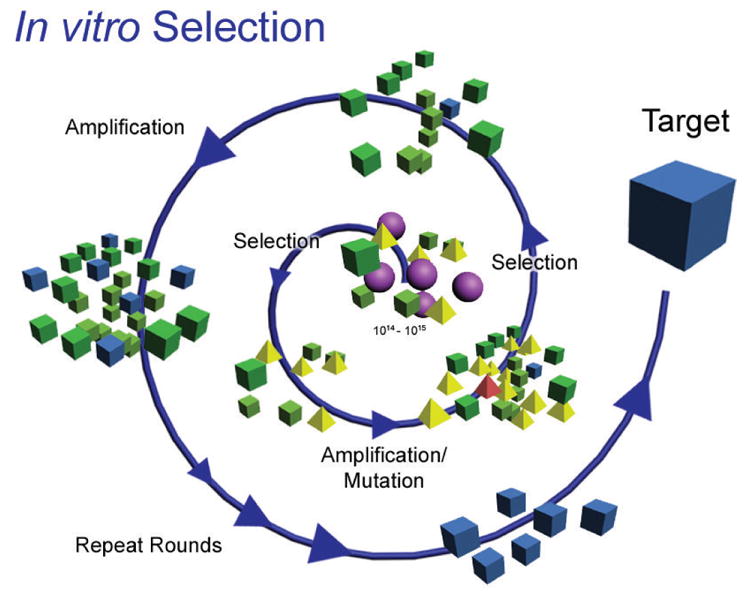
A representative scheme for in vitro selection of metal ion-dependent DNAzymes. A combinatorially large pool of random nucleotide sequences (center) with defined primer-binding regions is put through successive rounds of selection (activity towards the target metal ion of interest), amplification (using polymerase chain reaction, PCR), and mutation (using mutagenic PCR). Figure adapted with permission from ref 2
