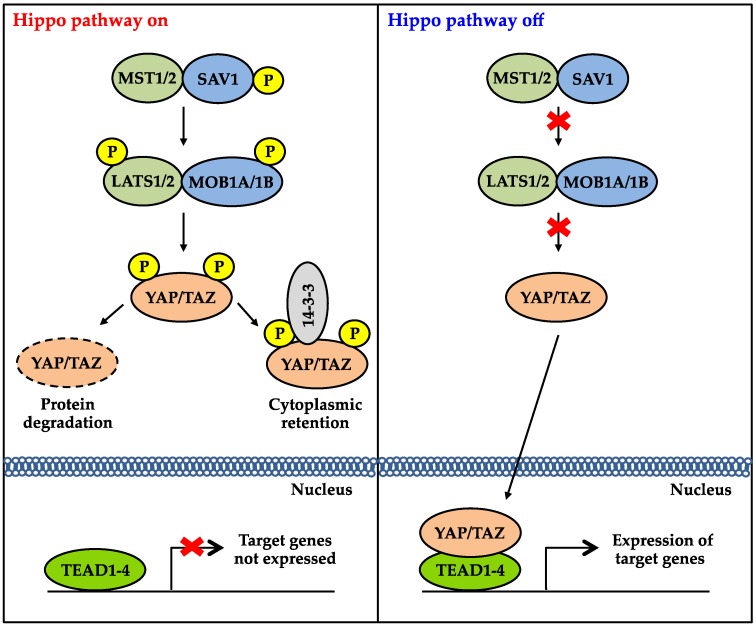
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the Hippo signaling pathway. (Left) When Hippo signaling is on, LATS1/2 phosphorylate YAP/TAZ, which leads to β-TrCP-mediated degradation of YAP/TAZ. Phosphorylation also promotes the retention of YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm due to the interaction with 14-3-3. (Right) When Hippo signaling is inactivated, YAP/TAZ accumulate in the nucleus and interact with TEADs, resulting in the expression of YAP/TAZ target genes.