Fig 1.
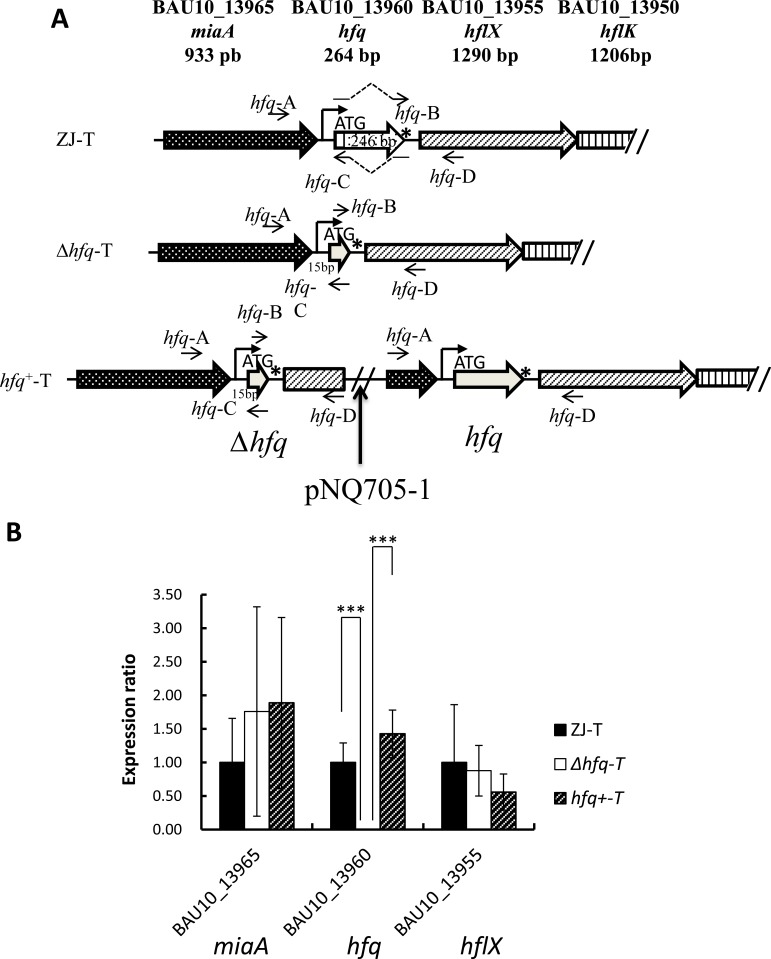
Structure of the hfq locus (A) and neighboring gene expression in Vibrio alginolyticus ZJ-T and derivative strains (B). A. The hfq gene is downstream of the miaA gene (locus ID = BAU10_13965) and upstream of 3 genes (hflX, K, C) likely to form an operon. A putative Sigma70 promoter identified upstream of hfq is indicated. 246 bps of the hfq ORF, from the 6th codon to the stop codon not included (marked by a star) were deleted as described in Materials and Methods, giving rise to the Δhfq-T strain. This mutation does not affect the potential promoter of the operon, neither the ribosome binding site of the downstream gene. A wild type hfq gene was reinserted at the Δhfq locus of the Δhfq-T strain by insertion of pNQ705-1-hfq by homologous recombination (see Materials and Methods for details) generating a duplication of the locus, corresponding to the fragment inserted in pNQ705-1, from primer hfq-A to primer hfq-D. The depicted situation corresponds to an insertion of the plasmid downstream of the hfq deletion. B. Relative expression of hfq, the upstream gene (miaA) and the downstream gene (hflX) in derivative strains compared to WT. Relative expression (normalized to the WT level for each gene) was determined by qPCR as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars correspond to standard deviations from three biological replicates. Statistically significant differences are indicated (***p < 0.001).