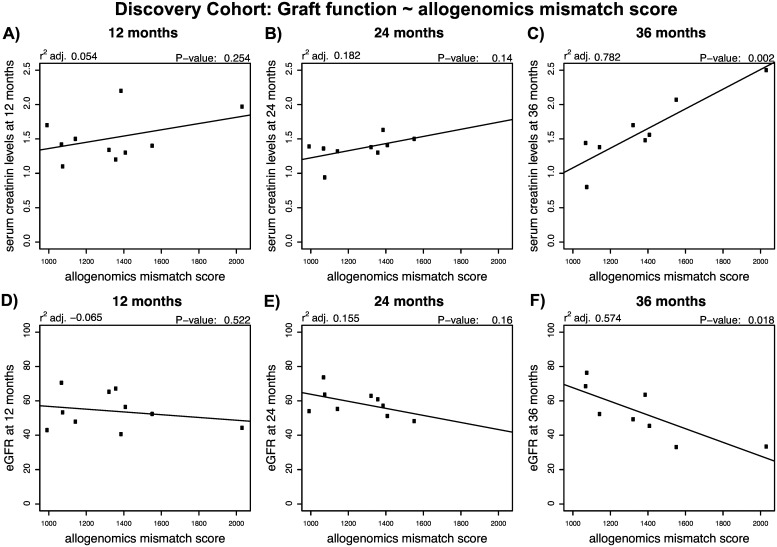
Fig 2. Relationship between the allogenomics mismatch score (AMS) and kidney graft function at 12, 24 or 36 months following transplantation in the Discovery cohort.
DNA was isolated from 10 pairs of kidney graft recipients and their living kidney donors (Discovery set). Whole exome sequencing of the donor genomes and recipient genomes was performed and the sequencing information was used to calculate allogenomics mismatch scores based on amino acid mismatches in trans-membrane proteins. The panels depict the relationship between the allogenomics mismatch scores and serum creatinine levels at 12, 24 and 36 months post transplantation (Panels A, B and C, respectively) and the relationship between the allogenomics mismatch scores and estimated glomerular filtration rate at 12, 24 and 36 months post transplantation (Panels D, E and F, respectively). Both serum creatinine levels and eGFR correlate in a time-dependent fashion with the allogenomics mismatch score with the strongest correlations being observed at 36 months post-transplantation.