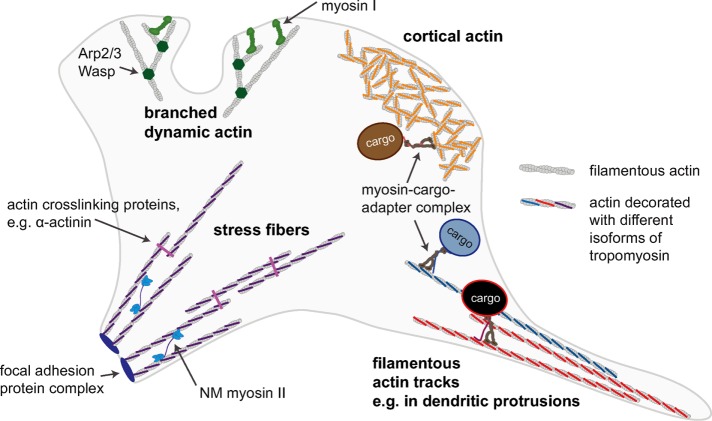
FIGURE 5:
Simplified schematic of a cell, illustrating the idea that different actomyosin processes in the cell may be spatially regulated by the “actin–Tpm code.” Actin structures with different functions and distinct Tpm isoforms bound will recruit only specific myosin motors. For example, the myosin-I isoform myo1b preferentially interacts with branched dynamic actin that is not decorated with Tpm, and there is evidence that other myosin-I isoforms show a similar preference (Ostap, 2008). Some nonmuscle (NM) myosin II isoforms interact with actin structures organized into stress fibers in a Tpm isoform–dependent manner (Ostap, 2008). We propose here that cortical actin and other filamentous actin structures decorated with different Tpm isoforms can act as selective transport tracks for motors such as myosin V and myosin VI.