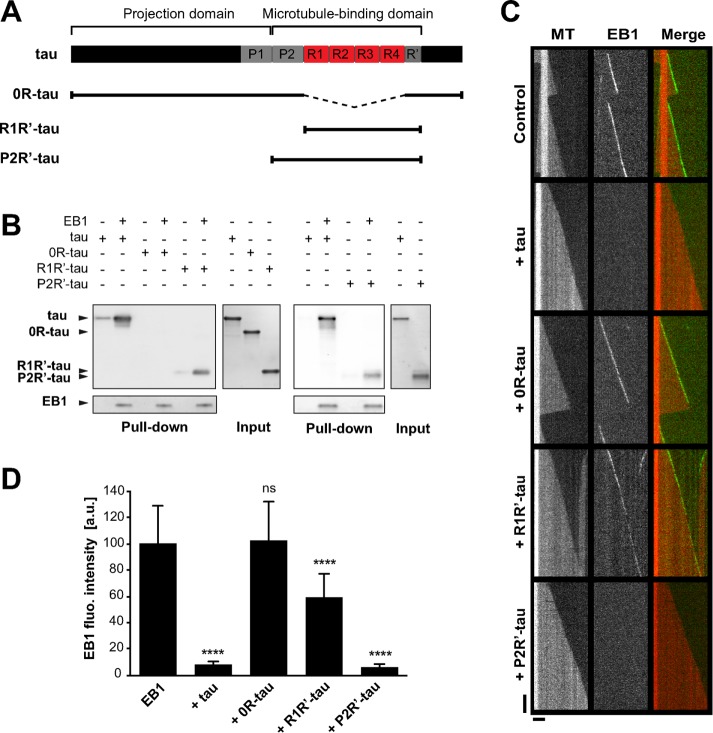
FIGURE 4:
EB1 interacts with tau microtubule-binding sites. (A) Schematic representation of full-length tau and the constructs used in this study. The N-terminal extremity and the proline-rich P1 region constitute the projection domain of tau. The microtubule-binding domain includes the second proline-rich P2 region, the tandem repeats (R1–R4). and the pseudorepeat motif (R′). (B) Pull-down assays of the indicated tau proteins with biotinylated-EB1. (C) Kymographs of individual microtubules growing with 75 nM GFP-EB1 in the absence (control) or presence of 75 nM indicated tau protein. MT, microtubule. (D) Fluorescence intensity of EB1 comets in the absence or in the presence of the indicated tau proteins. ****p < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant; nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunn’s comparison (32, 27, 42, and 35 microtubules for EB1, EB1 + tau, EB1 + 0R-tau, and EB1 + R1R′-tau, respectively) and Mann–Whitney U test (30 and 39 microtubules for EB1 and EB1 + P2R′-tau, respectively). The p values were calculated in comparison to the condition without tau. All error bars represent SD. a.u., arbitrary units.