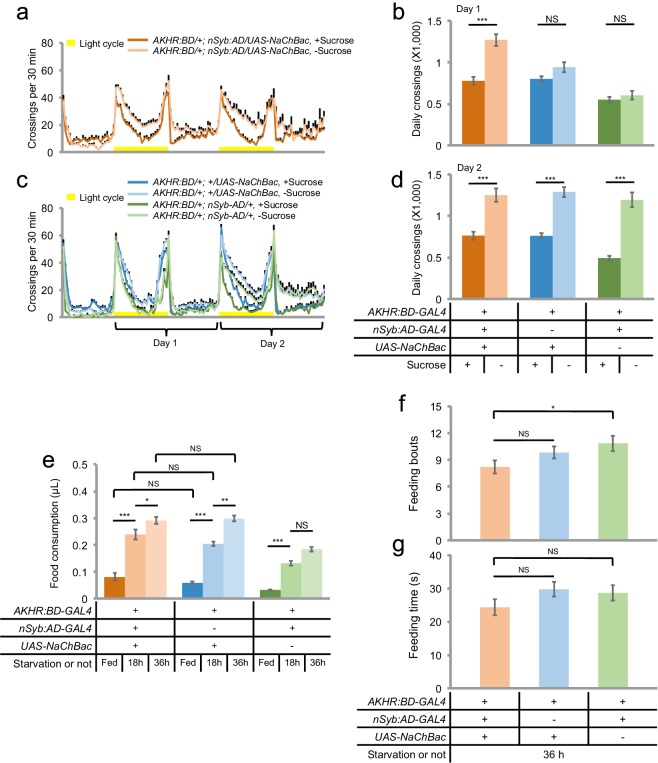
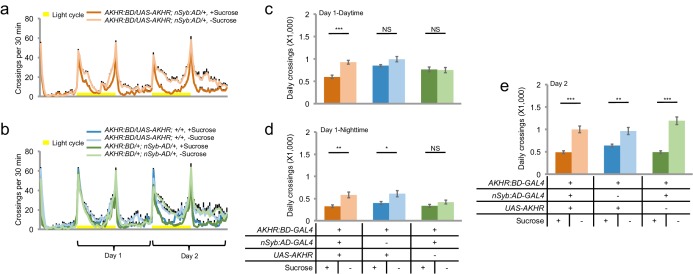
Figure 5. AKHR+ neurons promote starvation-induced hyperactivity.
(a, c) Midline crossing activity of indicated genotypes assayed in the presence of 5% sucrose ('+Sucrose') or 2% agar ('-Sucrose') (n = 48–80). (b, d) Average daily midline crossing activity during Day one (b) and Day two (d) of flies assayed in a, c. (e) Volume of 800 mM sucrose consumed in a meal by indicated genotypes fed ad libitum with 5% sucrose, or starved for 18 and 36 hr using the MAFE assay (n = 38–52). (f–g) Number of feeding bouts (f) and total duration of feeding time (g) during 1 hr recording in the FLIC assay (n = 54–60). Error bars represent SEM. NS, p>0.05; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.