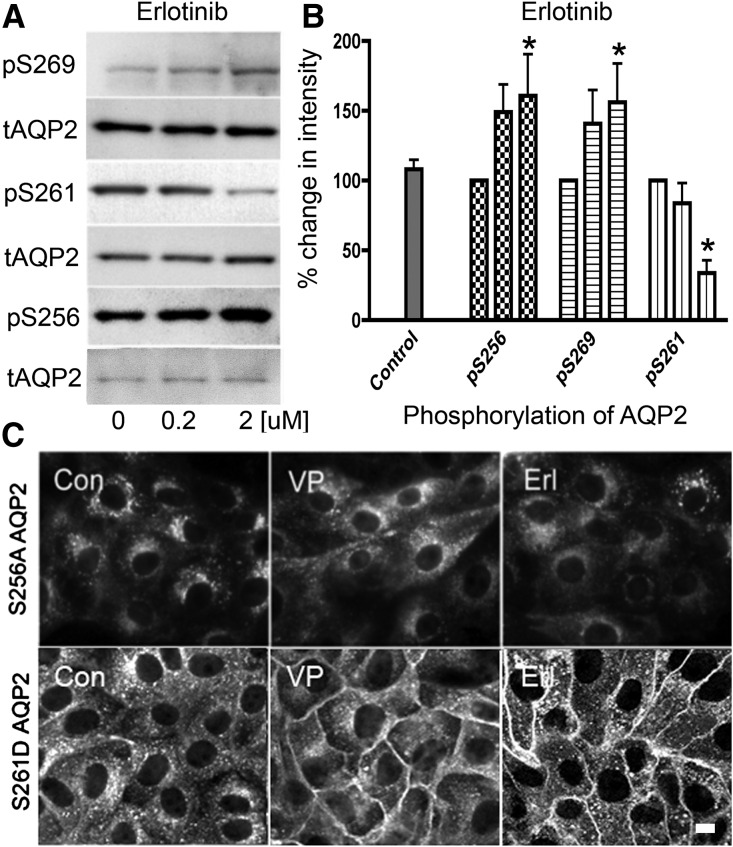
Figure 5.
The effect of erlotinib on AQP2 trafficking is Ser-256 phosphorylation dependent. (A) Western blots using specific phospho–AQP2 antibodies were performed on lysates from LLC-AQP2 cells treated with increasing amounts of erlotinib. Quantification is shown in B. (B) The phosphoserine band intensities were normalized by their respective total AQP2 loading controls (mean±SD; n=4). The data were analyzed using a two–way ANOVA Bonferroni post–test; pS256 and pS269 were increased by erlotinib, and pS261 was reduced (*P<0.05). The role of Ser-256 phosphorylation was also investigated using the LLC-AQP2 (S256A) mutant cell line. (C, upper panel) The VP–insensitive AQP2 mutant was not accumulated at the membrane when treated with VP or erlotinib (Erl). (C, lower panel) The role of Ser-261 was also studied using the LLC-AQP2 (S261D) mutant cell line. When treated with VP or Erl, there was an accumulation of this AQP2 mutant at the membrane. These results are representative of three independent experiments. Con, control. Scale bar, 10 μM.