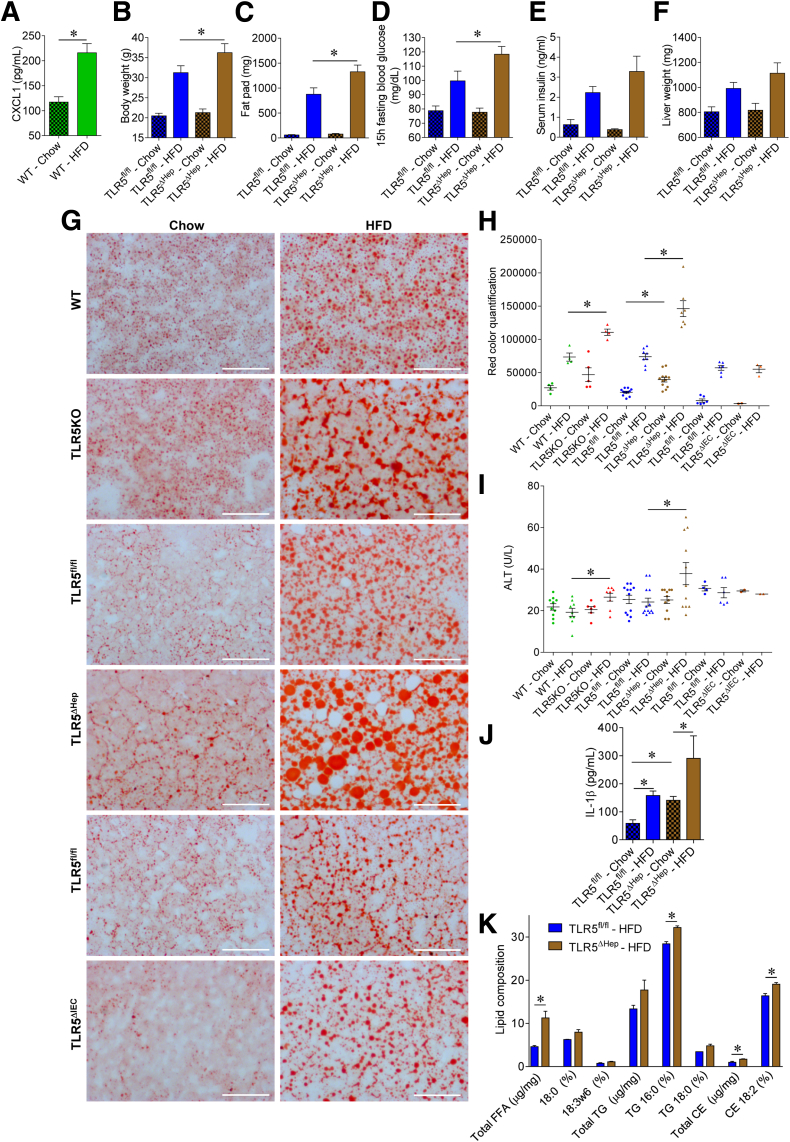
Figure 6.
Liver TLR5 protects against high-fat diet–induced metabolic syndrome and steatosis. (A) Analysis of CXCL1 protein expression level by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in sera of WT mice fed with a regular chow diet or a HFD, comprising 60% fat, for 8 weeks. (B–K) TLR5fl/fl and TLR5ΔHep mice were fed with a regular chow diet or a HFD, comprising 60% fat, for 8 weeks. (B) Body weight, (C) fat-pad weights, (D) 15-hour fasting blood glucose concentration, (E) 5-hour fasting insulinemia, and (F) liver weights were measured. (G and H) Liver lipid staining using Oil Red O, with (G) representative images and (H) quantification shown. (I) Serum ALT concentrations. (J) Serum IL1β concentrations. (K) Lipid composition in the liver. FFA, free-fatty acid; TG, triglyceride; CE, cholesterol ester. Scale bar: 50 μm. Data are the means ± SEM. (H and I) Points are from individual mice, with bar representing means ± SEM. N = 5–15. Significance was determined by the Student t test. *P < .05.