Figure 5.
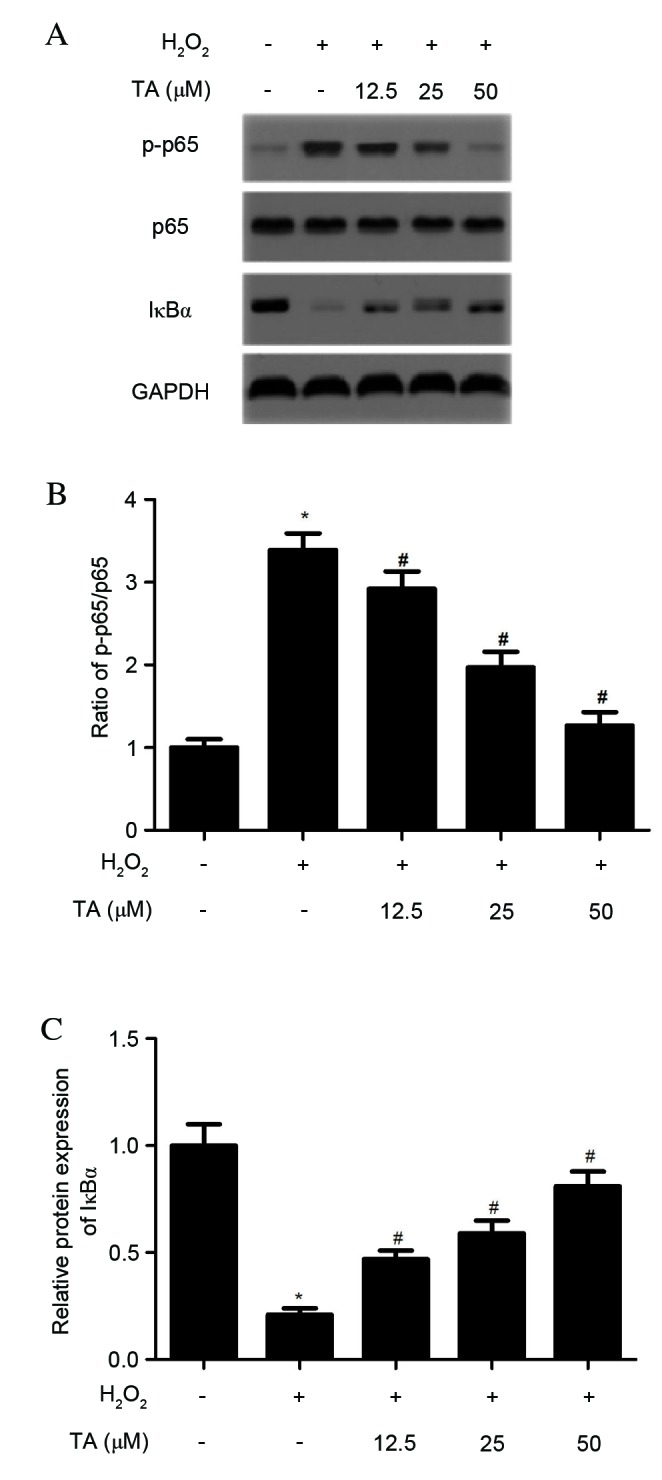
Effects of TA on the NF-ĸB signaling pathway in H2O2-induced RVSMCs. RVSMCs were pretreated with various concentrations of TA (0, 12.5, 25 and 50 µM) for 2 h, followed by the addition of H2O2 (final concentration 100 µM) for a further 24 h. (A) Proteins were subjected to western blot analysis to detect relative protein levels of NF-ĸB p65, p-NF-ĸB p65 and IĸBα, using GAPDH as the loading control. For each treatment, (B) the ratio of phosphorylated to non-phosphorylated NF-ĸB p65, and (C) the relative protein levels of IĸBα were analyzed. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation obtained from five individual experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05 vs. untreated control; #P<0.05 vs. H2O2-treated control. RVSMC, rat vascular smooth muscle cell; NF-ĸB, nuclear factor-ĸB; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; TA, tormentic acid; p-, phosphorylated; IĸBα, NF-κB inhibitor-α.
